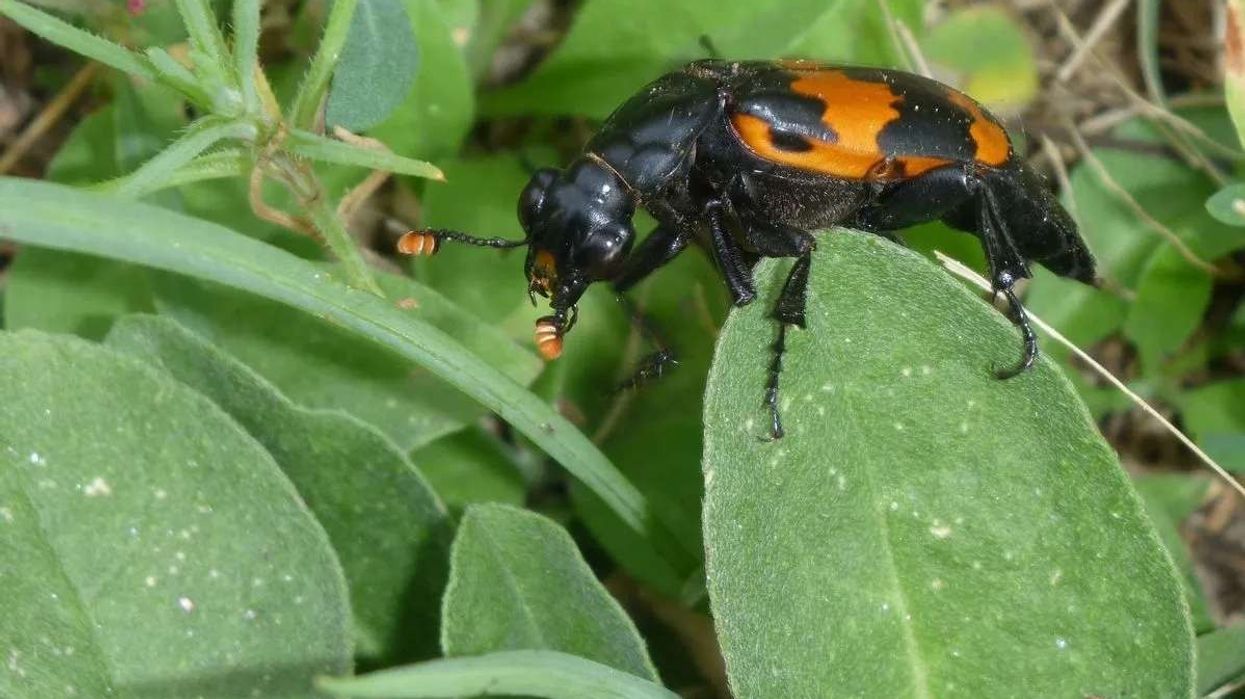
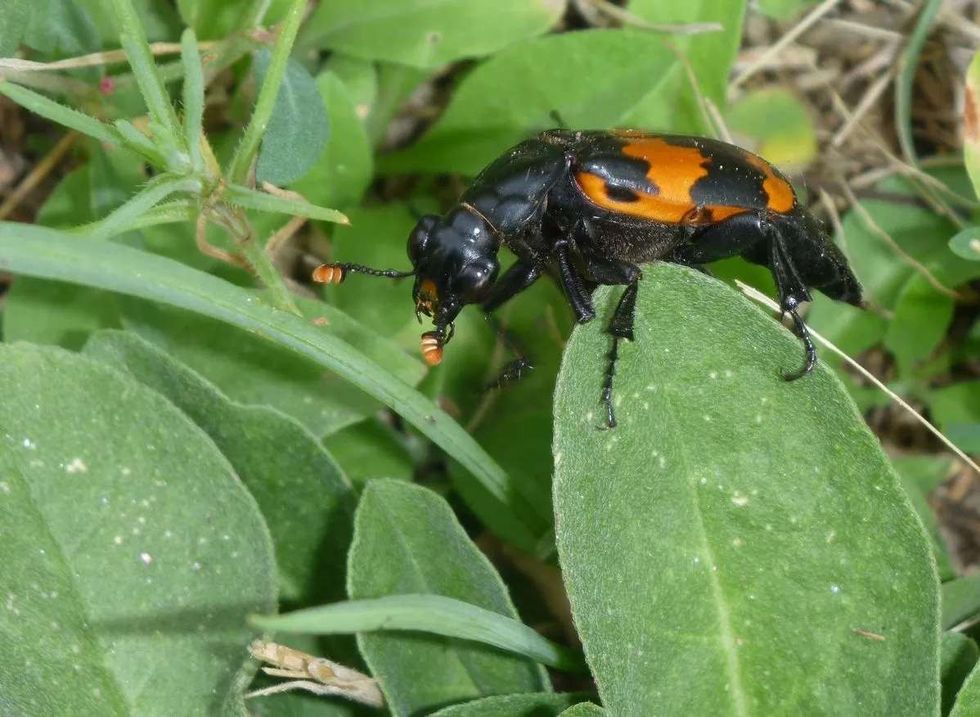
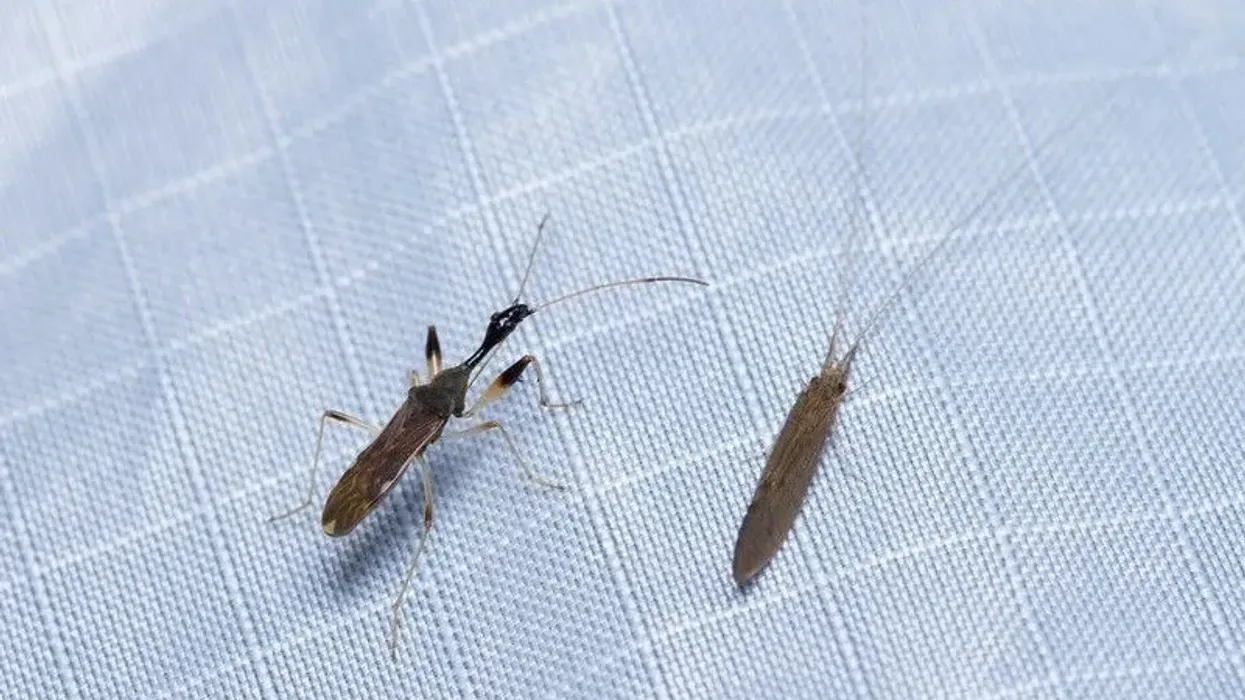
The burying beetle, or American burying beetle (Nicrophorus americanus), is also known as a giant carrion beetle and is a species that is around 1-1.5 in (2.5-3.8 cm) long with a distinctive appearance.
Their body is a shiny black color with orange-red markings just behind the head, and their wing covers are four scalloped and have large antennae with orange-colored clubs at the tips.
American burying beetles feed on the carcasses of dead animals and find their partners on the carcass too. Males attract females over the carcass and fight amongst themselves for the female here.
The victors mate with the female and bury the carcass in the soil. After this process, the female lays eggs near the carcass. The eggs hatch after three to four days and the larvae get plenty of food as they hatch inside the carcass and feed on it until they emerge as adults in around two months.
American burying beetles (Nicrophorus americanus) come under the category of Critically Endangered animals as they are threatened by habitat loss and diseases. As American burying beetles are nocturnal and travel at night, artificial lighting in their habitats also affects the population of these nocturnal insects.
Here are some amazing and interesting facts about American burying beetles for you to enjoy. Let's take a look at these American burying beetle facts and information, and if you enjoy these then you can read about the Green June beetle and atlas beetle too.
Burying Beetle Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a burying beetle?
The American burying beetle is an insect that feeds on the carcasses of dead animals and lays eggs near or inside these carcasses so that when their larvae hatch, they can have plenty of food for their nourishment. They're are the largest of all the carrion beetles.
What class of animal does a burying beetle belong to?
American burying beetles belong to the Insecta class.
How many burying beetles are there in the world?
Fewer than 1,000 American burying beetles are alive east of the Mississippi River. They can be found in various states including South Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and Arkansas.
Where does a burying beetle live?
American burying beetle populations live in open fields, grasslands, and forests. However, it is estimated and known that there are less than 1000 individuals alive right now, and because of this, they're considered a Critically Endangered species.
What is a burying beetle's habitat?
The American burying beetle has a wide range of habitats. They are found in different parts of North America, such as Rhode Island and Arkansas.
They prefer areas such as open fields or grasslands where the carcasses of dead animals are quite easily available. This allows male beetles to more easily mate with female beetles and provides a location for females to lay their eggs. After hatching, they are able to feed the larvae using this carcass too.
Who do burying beetles live with?
American burying beetles find their mates near the carcasses of dead animals. After, feeding, mating, laying eggs, and taking care of the larvae together, they go back into the soil alone.
How long does a burying beetle live?
The American burying beetles' life cycle is short, and adult American burying beetles live for just 12 months only. Due to various factors, including habitat loss, their populations have suffered a major loss in recent years.
How do they reproduce?
Male American beetles smell the carcass of dead animals, and when they reach it, female beetles are attracted to the male beetle's pheromones. Lots of burying beetles fight over the carcass, and the victors, usually the largest male and female, form a pair and mate.
The female beetle lays eggs near the carcass, and when the larvae hatch, both the male and the female take care of the larvae. Even though the larvae are able to feed themselves, the parents still bring food to them.
What is their conservation status?
The conservation status of the American burying beetle is Endangered. This is a critically endangered species. According to reports by the U.S. Fish And Wildlife Service, American burying beetles' (Nicrophorus americanus) populations have been decreasing over time due to many threats including habitat loss, pesticides, and artificial lights.
Burying Beetle Fun Facts
What do burying beetles look like?
The typical American burying beetle body is shiny black colored, with orange-red markings just behind the head. Their wing covers are four scalloped and they have large antennae with orange-colored clubs at the tips. They're the largest of all carrion beetles.
How cute are they?
The American burying beetle is not a particularly cute insect as it feeds off the carcass of dead animals and then mates near that carcass.
How do they communicate?
These giant carrion beetles use olfactory indicators located in their antennae to detect dead animals' carcasses, and males then release pheromones to attract females towards them. They can detect carcasses up to 2 miles (3.2 km) away. Males and females work in coordination to move and bury the carcasses in the soil.
How big is a burying beetle?
An American burying beetle is 1-1.5 in (2.5-3.8 cm) long. When compared to a common cockroach, they are about three times smaller than a cockroach. There aren't any known predators of American burying beetles and these beetles themselves do not try to prey on other insects very often, instead, they prefer dead animals' carcasses as their food.
How fast can a burying beetle move?
An American burying beetle is known as a strong flier and it can cover a distance of 0.62 miles (1 km) in a night which is a big feat for an insect this small.
How much does a burying beetle weigh?
The American burying beetle weighs only 3.5-7 oz (100-200 g). They're tiny insects and are very lightweight.
What are their male and female names of the species?
Males and females of these carrion beetles do not have separate names.
What would you call a baby burying beetle?
Baby burying beetles are called larvae and they usually hatch after three to four days. They are raised in the carcass, where both of their parents take care of them.
What do they eat?
This giant carrion feeds on the carcasses of dead animals. They use olfactory indicators in their antennae to detect dead or decaying flesh and fight for it.
The victor male and female get to eat the dead animal. They remove the fur or feathers from the carcass, bury it into the soil, and the female lays eggs above it so then when the larvae hatch, they can also get food from this carcass.
Are they poisonous?
These bright-colored insects are considered poisonous. The American burying beetle leaves a toxic smell to irritate other insects and animals and sends them a warning that they might be dangerous.
Would they make a good pet?
It is highly doubtful that they would make a good pet as their main source of food is dead animals, and after feeding, they go back into the soil. The species is also critically endangered, so you cannot keep them as a pet.
Did you know...
American burying beetles are classified as a Critically Endangered species. This is because they suffer from many serious threats such as a loss of habitat, the impact of artificial lighting, and human interventions in their habitats. For example, manmade things such as Keystone XL pipelines can threaten the existence of burying beetles.
The life history of these giant carrions states that they used to exist in 150 countries and 35 states in eastern and central United States. They now exist only in four states: Nebraska, Rhode Island, Oklahoma, and Arkansas.
Other than dead animals, they eat things such as rotten vegetables and sometimes even live insects too.
Have you heard of burying beetle mites? These mites live on burying beetles, and they form a symbiotic relationship.
Why is the burying beetle important?
Burying beetles are important as they are one of nature's best recyclists. They recycle dead animals' carcasses, which leads to the eventual return of highly valuable nutrients back to the earth.
They can even help in indicating whether the environment is healthy enough to live or not. This important role shows why we need to continue conservation efforts to save populations of this endangered species.
Who looks after burying beetle larvae?
Larvae hatch after three or four days, and even though they can feed by themselves, both parents look after them. They bring them food and take care of them. They leave regurgitated, half-digested food for the larvae to eat. After eating the carcass, larvae pupate into the ground and come out a month later.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! Learn more about some other arthropods, including the Hercules beetle, or water beetle.
You can even occupy yourself at home by drawing one on our Burying beetle coloring pages.