The Eurasian crane (common crane, grus grus) is typically found in Asia and Europe. They have recently been discovered in North America as well. This species of cranes considers an ideal habitat to be wetlands.
The diet for this species of cranes includes small birds. They communicate with a loud trumpeting call.
Their breeding season starts in spring. During their breeding season, this species of cranes make loud calls, and if they find a mate that has those similar calls, they stay together for life. Typically, Eurasian crane migration happens during the winter and these cranes move to northern Russia.
There are different breeds of these small birds and they can be found in different parts of Asia. They are fascinating to study as they have their own habits that are unique to them. For example, they tend to stay with the same mate for life.
Due to deforestation, their habitats are being destroyed. Conservationists in Europe are making a consistent effort to increase the population of this species.
They are kept in zoos and not as house pets as they like to stay in wetlands. You would not be able to mimic a wetland habitat in your house, so it is better to see these cranes in a zoo or in the wild if possible.
If you love birds, you can also read up on the crane and the blue crane too!
Eurasian Crane Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a Eurasian crane?
The common crane (Grus grus) is a type of bird. Its genus is Grus and this bird is part of the Gruidae family.
What class of animal does a Eurasian crane belong to?
The common crane (Grus grus) is part of the Aves class of animals.
How many Eurasian cranes are there in the world?
The population of these common cranes or Grus grus is more than 700,000. Their population was decreasing because of habitat loss, but now, their population has started to increase thanks to conservation efforts. Conservation efforts are taking place in parts of Asia and Europe. The main threat to these birds is humans as we are destroying their habitats.
Where does a Eurasian crane live?
The common crane bird (Grus grus) lives in wetlands and near rivers.
What is a Eurasian crane's habitat?
The common crane's favorite habitats are wetlands and rivers, as they like to forage for food. Their habitat is present in southern Europe, Asia, eastern China, and some parts of North America. They have recently been discovered in part of Alaska which is part of North America.
Who do Eurasian cranes live with?
The common crane bird (Grus grus) lives in flocks of its own species. These birds tend to be friendly with their own species and don't interact much with others.
How long does a Eurasian crane live?
The common crane has a lifespan of 30-40 years. They are known to survive better in the wild than in captivity, which is why efforts are being made to keep their habitats intact. Their habitats, unfortunately, are being taken over by human beings for agriculture.
How do they reproduce?
The breeding season for the common crane bird starts in April and goes on until June. The common crane tends to do a 'mating dance' during the breeding season and the partner that can mimic its dance is its partner for life.
The male tries to court the female with a series of 'dances'.
If the female bird notices that the 'dancing style' of the male bird is similar to hers during the breeding season, she will approach him. These common crane birds produce about one or two eggs during the breeding season.
What is their conservation status?
The common crane, which can sometimes be found in the northern part of America, has a conservation status of Least Concern according to the IUCN Red List. The population of this bird has been increasing thanks to conservation efforts happening in Europe and some parts of Asia.
Eurasian Crane Fun Facts
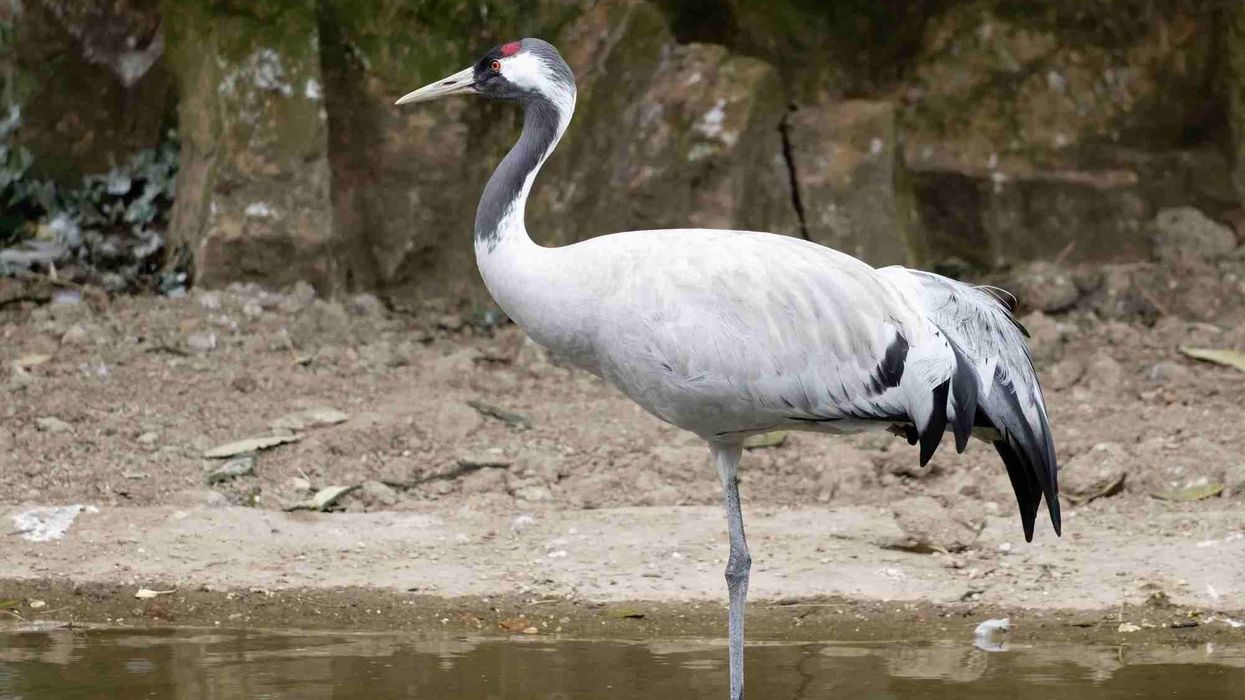
What do Eurasian cranes look like?
You may have heard about the red-crowned crane? Well, though different, an adult common crane has a red crown too. A family of these birds can be differentiated by their color tones.
When in flight, their wings can be as long as 82.6 in (209.8 cm). They are found in some parts of Europe and southern Asia, more specifically in southern China. They have recently been noticed in northern America as well.
A chick does not have a red crown. The adult's plumage is gray, whereas the chick's plumage is a lighter gray.
The adult's neck is dark gray or black. When the chick gets a little older, you can notice its gray feathers getting darker in some areas, especially the neck. This bird has a distinct call during its breeding season; it attracts a mate with this call.
This crane is not very colorful but is known for how high it can fly. These birds have long wings that help them reach great heights. They need this quality during their migration season, which typically happens during the winter. They can not tolerate the cold and that's why they travel to warmer places to survive.

How cute are they?
The common crane is not really cute. These birds are considered to be more elegant than cute. In comparison, the Siberian crane could be considered cuter.
How do they communicate?
The common crane communicates with a loud trumpeting call. You can hear this call normally in the morning. This is a call that only other common cranes understand.
How big is a Eurasian crane?
The common crane is big compared to other cranes. For example, the sandhill crane is 54 in (137 cm) whereas the common crane is 52 in (132 cm). In comparison, the Sarus crane is around 35-51.1 in (88.9-129.7 cm) long.
How fast can a Eurasian crane fly?
The speed of flight for the common crane is stated to be about 25-35 mph (40.2-56.3 kph). They can travel up to 300 mi (482.8 km) per day.
How much does a Eurasian crane weigh?
The common crane weighs 12 lb (5.4 kg).
What are the male and female names of the species?
The male is called a cock and the female is called a hen.
What would you call a baby Eurasian crane?
A Eurasian crane's juvenile is called a Eurasian crane chick.
What do they eat?
The common crane (Grus grus) preys on small birds and mammals like frogs, snakes, and lizards. They are known for foraging for leaves and plants in the water as well.
Are they dangerous?
No, these cranes are not dangerous.
Would they make a good pet?
No, they wouldn't make a good pet as they like to live in wetlands.
Did you know...
The common crane (Grus grus) was extinct from the UK in the 17th century.
Can you eat a Eurasian crane?
No, you cannot eat this species of cranes. The species of crane that you can eat is the sandhill crane.
How high can Eurasian cranes fly?
This species of cranes can fly up to 33,000 ft (10,058.4 m) high. They are known to fly up pretty high and travel during their migration to long distances.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these sea eagle facts and crested duck facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable duck coloring pages.