The European badger (Meles meles) is one of the biggest badger species in the world found majorly in European countries and parts of Asia.
The European badger is also called the Eurasian badger (Meles meles) and is mostly found living in Europe, its habitat includes temperate ecosystems like savannas, mixed and coniferous woodlands, deciduous woods, and even urban and suburban areas.
The class order of these badgers is Mammals, and when it comes to the kingdom/phylum, they belong to the Animalia kingdom and Chordata phylum.
The mating season of these badgers is throughout the year but is most active in the spring, late summer, and winter.
The male badgers face risk in entering the setts while females move to other setts, searching for males for mating.
European badgers are known to be aggressive animals and feed on smaller mammals, insects, and occasionally plants and fruits. To know interesting facts about this animal, keep reading.
If you liked reading about these facts, you could also check other facts on the black-footed ferret and the oncilla.
European Badger Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a European badger?
The European badger or the Eurasian badger is one of the badger species of the Mustelidae family. These are called so as they are native to almost all parts of Europe and some western parts of Asia.
These animals are found only in European and Asian countries and are quite rare as they live in a specific habitat with natural conditions.
What class of animal does a European badger belong to?
The European badger (Meles meles) species, just like other badger species, belongs to class Mammalia as they give birth to young ones. They belong to the Mustelidae family and are famous for their black and white stripes on the body. Being a part of the Animalia kingdom.
How many European badgers are there in the world?
The exact population of the European or the Eurasian badger (Meles meles) is not known. Still, according to sources, about 30,000 adult individuals were recorded in 1990, and since then, the population has been increasing.
They are abundant and are currently under the Least Concern category of conservation status.
The living condition of these badgers are quite simple, and they do well in the wild and give birth to about one to five young in a breeding season.
Though these badger species are good in number across the globe, they are already exposed to many human and natural threats that directly target their population and bring it down by huge margins every year.
According to studies and records, some of such threats are hunting, habitat loss, industrial developments, and road accidents Almost 40,000 European badgers die every year because of road accidents.
Where does a European badger live?
The European badger habitat majorly includes coniferous and mixed woodlands, deciduous woods, temperate ecosystems, spinneys, pasture land, scrub, and savannas. They are majorly found near water bodies, and as the European badger diet includes mostly insects, small mammals, and earthworms, they are found in places above three in good numbers.
Although it is a carnivore, it is also seen feeding on many fruits like berries. These badgers generally live on land and search for food on the same.
The European badger adaptations help it live even in suburban and urban areas. These badgers (Meles) live in underground homes known as setts that help them to hunt their prey and be safe easily and be safe from their predators.
These badgers are known to live in an underground home which is called a sett. The sett is made when the badger (Meles) sows the ground.
What is a European badger's habitat?
The European badger's natural habitat includes regions like pasture land, scrub, savannas, coniferous woodlands, deciduous woods, spinneys, and temperate ecosystems. All of the above are rich in their food sources for earthworms, insects, and small mammals.
Apart from feeding on animals, worms, and insects, these badgers are also known to eat fruits like berries occasionally in the wild. These badger populations are powerfully built, and because of their adaptive nature, they are even found in urban and suburban areas.
Who do European badgers live with?
The Eurasian badger (Meles) lives in groups of about six members, which include both adults and young badgers. If you wonder, is the European badger territorial?
The answer is yes, these badgers are very territorial and become aggressive if someone tries to enter their territory or if they feel threatened. These badgers live in underground setts and are known to move and hunt for food together.
How long does a European badger live?
The European badger's lifespan in the wild is about 15 years. The lifespan of these badgers may vary from place to place as there are a lot of things that threaten their life.
Honey badgers are known to live for about 24 years in the wild. These badgers are known to do well in captivity, too, as they can live for nearly 20 years or more in captivity.
How do they reproduce?
The European badger's mating habits are quite interesting and different from other mammals. These badgers are promiscuous and can mate with other clan individuals.
Males face great risk while searching for mating with females in other sows or setts. Females are generally seen moving into other badger territories and setts where they can frequently mate with other badgers (Meles).
The breeding season of the Eurasian badgers is from spring or late summer (February to May), and the implantations are mostly done during the winter in December. The European badger baby is born after a gestation period of about seven weeks in February or March.
Cubs are born in underground setts of chambers that contain bedding. The mating of these badgers (Meles) can happen throughout the year in the wildlife.
Cubs are born mostly at the start or end of the year (Spring or winter). The female gives birth to about one to five young cubs, and the male protects the female and brings food.
These badgers (Meles) are sexually active throughout their range but most active during the late summer, winter, and early spring. The young cubs prefer to stay close to females (mothers) and become adults after a period of eight to 10 months.
What is their conservation status?
The current status of the conservation of this badger (European) is Least Concern. Due to various reasons like hunting, accidents on roads, developments, and habitat loss due to various natural and human reasons, the population of badgers has been going down in huge numbers over the years.
However, the badger population is increasing and in good numbers, too.
This is due to their ability to give birth to up to five cubs every time they breed, which has, in turn, helped them slip under the Least Concern tag. Therefore, they do not need much attention as they are neither endangered nor vulnerable.
European Badger Fun Facts
What do European badgers look like?

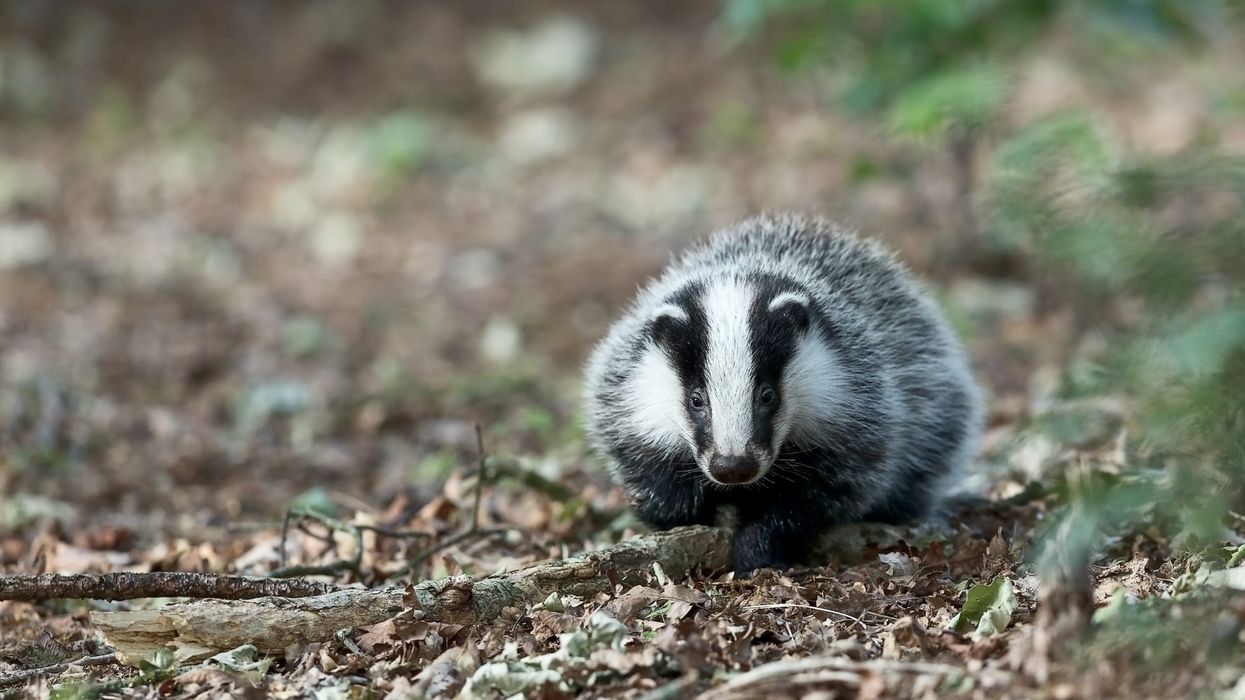
The European badger is reddish-brown, black, and white with a stocky body. The European badger's front paws are massive and look like a shovel and have five powerful toes, each topped with steel-like claws that help them hunt and dig dominant sows and their sett.
The European badger's underbelly and short tail are generally lighter in color than the rest of the body. The badger (Meles) has thick skin, which helps it withstand various natural conditions and keep it warm.
These badgers have black noses and eyes. The European badger's teeth are flatter, which helps them grind plants and also prey on smaller mammals and large insects.
How cute are they?
These badgers are somewhat cute as they are small animals, and the white markings on the head of these animals give them a unique and attractive look. Baby badgers are the cutest.
How do they communicate?
The Eurasian badger communicates in many ways, which include postures and visual stances to show aggressive behavior. Scraping their hind legs and raising their tails is also a way to show aggression. They also use a range of vocals to communicate in groups.
How big is a European badger?
The European badger's body size is of length 24-35 in (60-90 cm) and its height is 11.8 in (30 cm). They can be 10-12 times smaller than a bear, which is also one of their predators.
How fast can a European badger run?
Eurasian badgers have a running speed range between 16-19 mph (25.7-30.5 kph).
How much does a European badger weigh?
These badgers have a weight range of 15-37 lb (7-17 kg).
What are the male and female names of the species?
Males are called boars, whereas females are referred to as sows.
What would you call a baby European badger?
A baby European badger is called a cub.
What do they eat?
These badgers eat insects such as caterpillars and ground beetles, and smaller mammals such as mice, shrews, rabbits, earthworms, plants, and fruits. These badgers can eat about 3.4% of their body weight every day.
Are they aggressive?
Although these animals are quiet, they can be very aggressive and dangerous if they feel threatened and can even attack their predators. They are, however, reluctant to interact with humans and therefore are not dangerous or aggressive towards humans.
Would they make a good pet?
The European badger pet is not a great choice for a pet as they are wild animals and can be very dangerous and unpredictable.
Did you know...
The European badger skull is massive, elongated, and heavy.
The European badger's bite can cause serious damage to its enemies or prey and even turn out to be fatal.
The European badger's hind legs help them move fast and also in building a sett.
The Eurasian badgers have a keen and amazing sense of smell, especially when they dig down for rabbit nests.
European badgers are very clean and clear out old bedding regularly.
European badgers are the only ones that can kill and then eat hedgehogs because they have very long claws and thick skin!
The European badger's tail is very short and raised during fights or when they are sexually excited. This species of badgers use their shovel-like front paws with sharp claws to build sett and hunt a wide variety of mammals and insects.
These badgers can be commonly found in Europe, where other badger species are not found. This species of badger are known to have a thick line on its skull, but its reason is unknown.
How old can European badger sets be?
The setts made by families are well-suited for future generations, and these setts can be more than 100 years old.
What was made illegal concerning European badgers in 1835?
Badger baiting was a popular blood sport in earlier times which was banned in 1835 as it affected the population of this animal.
North American badger vs. European badger
The European badger is taller and larger than the American badger.
European badger vs. Honey badger: Honey badgers are lighter and shorter than European badgers.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! Learn more about some other mammals from our fox facts and Bengal tiger facts pages.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable European badger coloring pages.