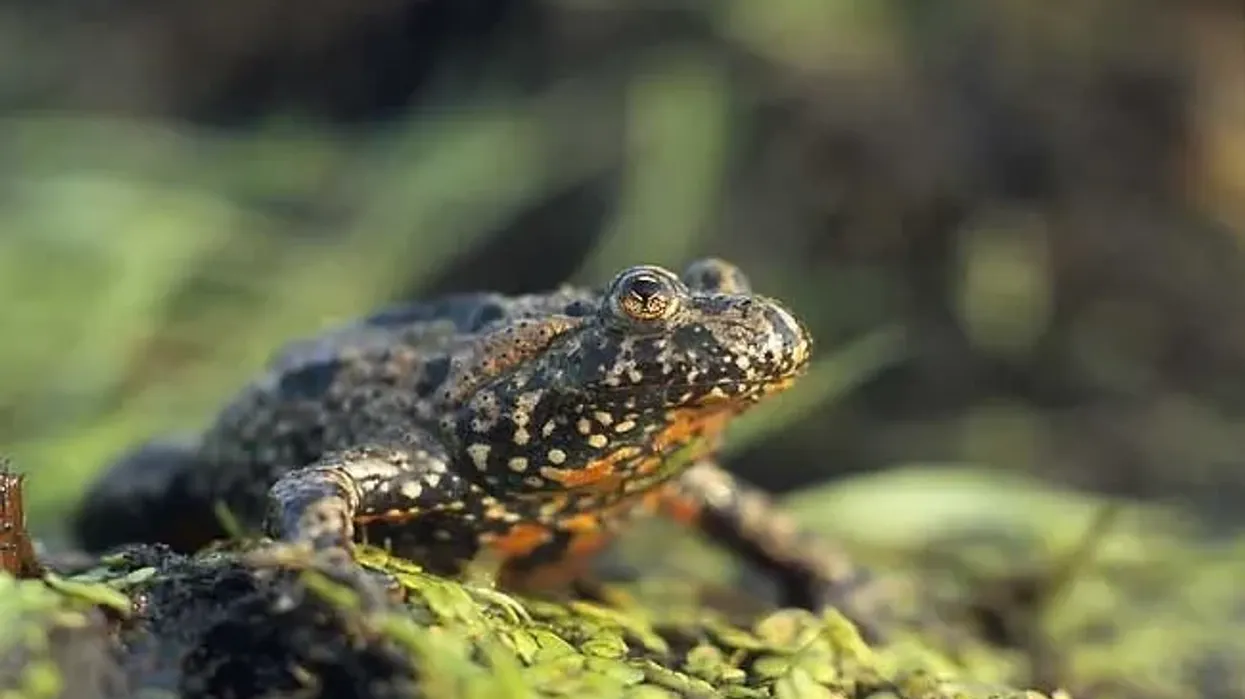
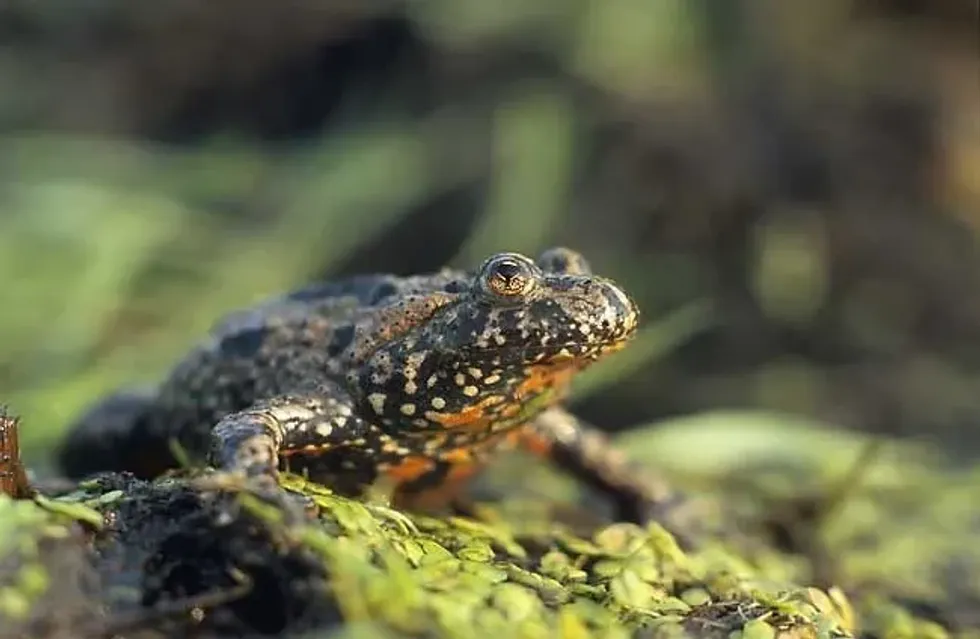
The European fire bellied toad (Bombina bombina) is a semi-aquatic amphibian, native to Europe. They are a part of the Bombinatoridae family. This toad and other members of the fire bellied toad group are called so, due to their red or yellow-colored bellies, which warns predators of their toxic nature.
These toads are commonly found in wetlands, forests, and water bodies like streams, ponds, and ditches. European fire bellied toads assume a threatening position when under attack.
They either protrude their brightly colored belly upwards or downwards, to show predators their warning coloration. These toads are very popular as pets, due to their bright colorations and minimal requirements. Even though they are toxic in nature, the poison secreted by their skin is not fatal to humans.
Nevertheless, they should be touched as little as possible, and should only be handled with utmost precaution. The European fire bellied toad is darker in color than the fire bellied toad found in Asia, for example, the Oriental fire bellied toad (Bombina orientalis).
To learn more about the Europan fire bellied toad, keep reading! If you like this article, you can also check out these western toad facts and Wyoming toad facts.
European Fired Bellied Toad Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a European fire bellied toad?
The European fire bellied toad (Bombina bombina) is actually a small frog species. However, these frogs are commonly known as toads due to their warty skin.
One of the main differences between frogs and toads is that toads usually have drier and bumpier skin than frogs, who have moist and slimy skin. The European fire bellied toad and other members of the fire bellied toad group are one of the exceptions to this.
What class of animal does a European fire bellied toad belong to?
These frogs are amphibians who belong to the class Amphibia. The word 'amphibian' was derived from the ancient Greek word 'amphíbios', which translates to 'both kinds of life'. These animals are called so as they live both in water and on land.
How many European fire bellied toad are there in the world?
The exact population of the European fire bellied toad is unknown, but their numbers are decreasing in the wild. In some regions of Europe, their population is quite widespread, like in the northern and western parts of the Danube floodplain.
However, in Denmark and Sweden, their numbers are low. In 2008, 10,000 adults of this species were accounted for in Sweden.
Where does a European fire bellied toad live?
European fire bellied toads are native and endemic to Europe. They are mostly found in the Central and Eastern parts of Europe. Some of the countries where these toads are found are Greece, Germany, Bulgaria, Croatia, and Denmark. Their population was introduced in the United Kingdom.
What is a European fire bellied toad's habitat?
The habitat of European fire bellied toads consists of forests, water bodies, and wetlands. They are known to inhabit marshy or grassy wetlands with lakes and ponds.
They can also be found in stagnant waters like ditches and swamps, or semi-flowing waters like springs and streams. In their southern range, they have also adapted to living in polluted water. Their forest habitat includes steppe, mixed leaf, and broad-leaved coniferous trees.
In case these toads are living in open landscapes, they use drainage channels for their dispersal. These toads are more active during warmer temperatures.
Who does the European fire bellied toad live with?
European fire bellied toads are known to live in groups consisting of dozens of members. Such groups are known as knots. These toads are also popular as pets, so they can live with humans too.
How long does a European fire bellied toad live?
In the wild, these toads can live as long as 12 years. In captivity, they can live for nearly 20 years.
How do they reproduce?
The breeding season starts in May and lasts till the end of the summer season. During this time, male toads produce mating calls to attract a potential mate.
The females lay 80-200 eggs. The fertilized eggs are attached to plants and young tadpoles hatch out in the water after two to five days. The metamorphosis of these tadpoles lasts from June to September.
What is their conservation status?
These toads are not endangered. The conservation status of the European fire bellied toad has been marked as Least Concern.
However, these amphibians are threatened by habitat loss and degradation of wetland ecosystems. Climate change also affects their population. Hybridization with another member of the genus Bombina, Bombina variegata or yellow-bellied toads, also leads to a decline in true European fire bellied toad populations.
European Fire Bellied Toad Fun Facts
What does European fire bellied toads look like?
The European fire bellied toads (Bombina bombina) have quite a distinct appearance, both during their young and adult life stages. Tadpoles are brownish in color with pale bands along their backbones.
In adult toads, the body is usually gray, green, or brown in color with prominent dark spots. However, in muddy water with riparian vegetation, toads of this species can be seen with a bright green dorsal surface. Their belly is bright red or orange in color with dark and white spots.
Their inner legs are also covered with small and bright spots. The legs are webbed which helps with their semi-aquatic nature.
The skin type in these toads is tuberculate. They have spines on their skin which gives the skin a bumpy feel. Their eyes are set high above with heart-shaped pupils.
The mouth is triangular in shape. The male amphibians of this species can be distinguished due to their slightly larger head.

How cute are they?
European fire bellied toad species can be considered cute due to their brightly colored appearance. Their bellies have a mixture of bright red or orange spots, which certainly adds to their charm. These amphibians are quite popular as pets, due to their colorations.
How do they communicate?
European fire bellied toads primarily communicate through different calls, vocalizations, and visual means. During the breeding season, the male toads of this species produce calls while floating on the water surface, or from underwater.
Each call is usually repeated 10-50 times by the toad. They are able to produce this sound by using their vocal sac.
The vocal sac is located inside the mouth of the male European fire bellied toads. Members of this species also assume a position known a unkenreflex, when threatened by predators.
They do so by turning over and protruding their brightly colored bellies upwards and covering their eyes. Alternatively, they also resort to curving their body downwards and showing the red or orange colorations on their body.
How big is a European fire bellied toad?
The length of the European fire bellied toads is between 1-2.3 in (2.5-5.8 cm). This species of toad from the fire bellied toad group is slightly smaller than another species of the group, known as the Oriental fire bellied toad (Bombina orientalis), which has a length between 1.5-2 in (3.8-5 cm).
When compared to the spadefoot toad, which is 1.6-3.1 in (4-7.8 cm), it seems to slightly similar.
How fast can a European fire bellied toad swim?
The exact swimming speed in European fire bellied toads is not known. However, toads of the fire bellied group are not very adept at swimming. They tend to remain submerged.
How much does a European fire bellied toad weigh?
The weight of the European fire bellied toad (Bombina bombina) is between 0.07-0.4 oz (2-13.9 g).
What are the male and female names of the species?
The male and female toads of this species are known as male European fire bellied toads and female European fire bellied toads, respectively.
What would you call a baby european fire bellied toad?
Baby European fire bellied toads are known as tadpoles.
What do they eat?
The European fire bellied toad, Bombina bombina, has an omnivorous diet. Some of the common food materials in their diet are insects, earthworms, mollusks, spiders, worms, and millipedes. Additionally, they eat plants and algae. Bacteria and plankton are part of the food materials in tadpoles.
Are they poisonous?
European fire bellied toads, just like the other species of fire bellied toads, are poisonous in nature. The skin in these toads produces a kind of poison or toxin, that acts as protection against predators.
The orange or red coloration of these toads is a warning sign to predators about the toad's toxic nature. In humans, it does not cause death but the toxin can cause harm if it comes in contact with someone's mouth, broken skin, or eyes.
Would they make a good pet?
These toads are quite popular as pet animals. They are quite easy to keep as pets, as their requirements are minimal. However, all species in the fire bellied toad group, including the European fire bellied toads, secrete a toxin or poison through their skin. This adaptation is mainly to deter predators in the wild.
However, it can cause irritation to humans as well. Hence, these toads shouldn't be touched too frequently. It is also advisable to wear gloves when handling these toads and washing your hands right after.
Did you know...
These animals eat their own skin, which they shed, in order to get nutrition.
Unlike most other common toads, European fire bellied toads make a 'bark' sound as part of their mating call.
Night herons are common predators of European fire bellied toads, who eat these animals, despite their toxicity and warning coloration.
Are fire belly toads endangered?
Four species of fire bellied toads have been listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature or IUCN, all with decreasing population trends. Out of the four species, three have been marked as Least Concern (Oriental fire bellied toad, European fire bellied toad, and yellow-bellied toad), while one has been marked as Endangered (Apennine yellow-bellied toad).
These toads are mainly threatened by habitat loss and climate change.
In Apennine yellow-bellied toads, the disease chytridiomycosis is suspected to be a major cause of the decline in population. The Oriental fire bellied toad (Bombina orientalis) faces threats from being used in traditional Chinese medicines.
Can toads drown in water?
All kinds of toads, including the fire bellied toads, are capable of breathing underwater through their skin. However, if the water does not have sufficient oxygen for these animals to absorb, they will end up drowning. Additionally, since toads also have lungs, if their lungs are filled with water, that will also result in drowning.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these cape rain frog facts and oak toad facts pages.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable fire-bellied toad coloring pages.