Galago monkeys are regarded as Lorisidae's sibling group. Prior to 1980, only six species from this genus were recognized.
However, researchers since then have found up to 20 species of this family galagidae. Galago monkeys are small nocturnal primates that are endemic to Sub-Saharan African regions like Southern Africa, Central Africa, South Africa and East Africa.
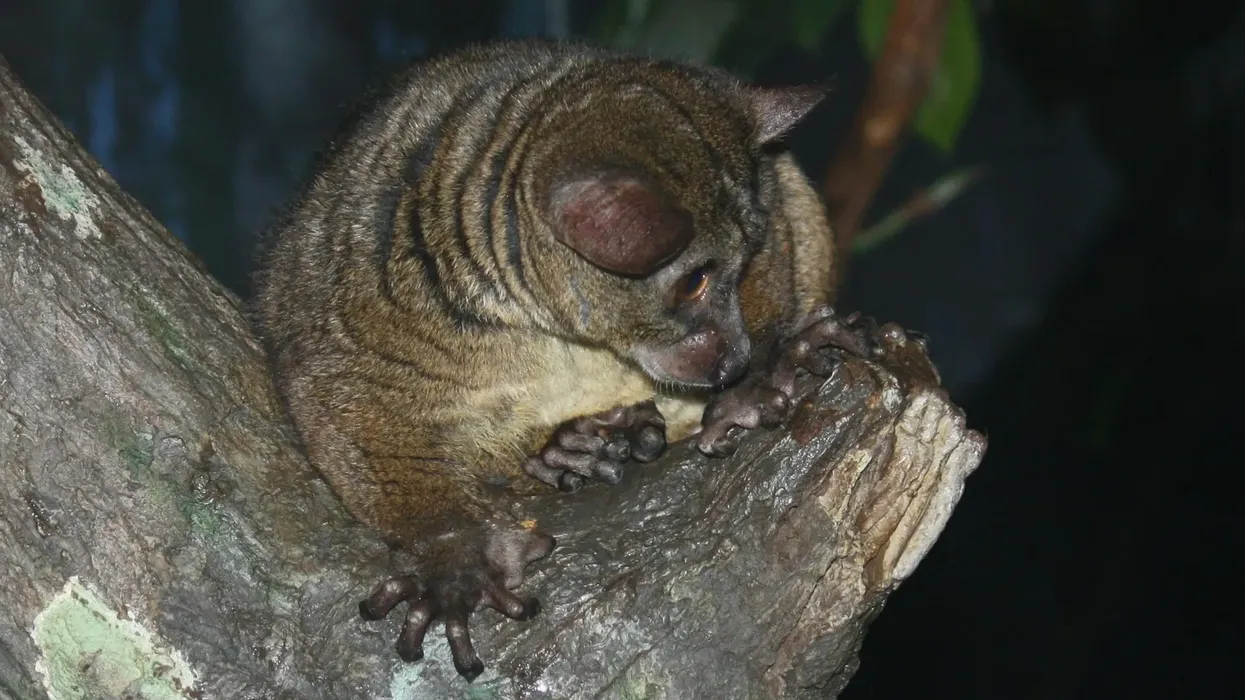
These bush babies have enormous eyes and ears, long hind legs, soft, fuzzy fur, and long tails and are gray, brown, or reddish to yellowish-brown.
The term bush baby refers to the animal's screams or its look. Because of the strong grasp on branches, greater galago monkey species is also known as aposor in Ghana.
Some of the most well-known subspecies for these animals are lesser bushbabies (galago senegalensis), brown greater galago (otolemur crassicaudatus) also known as large-eared greater galago or thick-tailed galago, and the lesser bushbabies (galago moholi). Here are some interesting facts on the greater galagos for your perusal.
Afterwards, do check our other articles on tamarin monkey facts and titi monkey facts.
Galago Monkey Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a galago monkey?
Bushbabies are tiny nocturnal primates endemic to southern and sub-Saharan Africa. Brown greater galago (otolemur crassicaudatus) are members of the galagida family. Greater galagos (genus genus galago) are found in forests of Southern Africa, ranging from southern Sudan to eastern South Africa and Angola. This primate species is known to look for food only at night.
What class of animal does a galago monkey belong to?
A galago monkey belongs to the mammals that give birth to their young ones of the family Galgida. The most widespread species of this primate family are subspecies for these animals are lesser bushbabies (galago senegalensis), brown greater galago (otolemur crassicaudatus) also known as large-eared greater galago or thick-tailed galago, and the lesser bushbabies (galago moholi).
How many galago monkey are there in the world?
There are no exact estimates of the population of the bush babies as well as the thick tailed greater galago in the wild habitats across Southern Africa, Central Africa, South Africa, East Africa. The conservation status of this species varies from least concern to critically endangered across their range of habitat across the forests in the world.
Where does a galago monkey live?
Population of these bushbabies may be found in woods throughout Sub-Saharan Africa. Some species, such as the South African galago, spend their time on the savanna among acacia trees. This primate species from genus galago is active only at the night. Their habitat can be found in Southern Africa, Central Africa, South Africa and East Africa.
What is a galago monkey's habitat?
Some species, such as the South African galago, congregate on acacia trees on the savanna. Other species, like the brown greater galago, require more tropical and subtropical woodlands, but the Somali galago may be found in dry, thorny areas of their habitat world.
Who do galago monkey live with?
Small creatures, such as frogs and birds, are hunted by some of the bigger galago species. These primates live in small family groups.
The number of individuals in family groups range between two to seven individuals. These family groups may or may not feature the young ones. The groups will often spend the day curled together in their hole but will separate at night to search for food.
How long does a galago monkey live?
Captive life span for the greater galago bush baby species is in the range of 12-16 years. The wild life span for the species is in the range of around four to five years at the most.
This data suggests natural longevity of more than a decade in captivity for the thick tailed greater galago busy baby, according to the South African veterinary and zoological data.
How do they reproduce?
Galagos are polygynous breeders in general across their breeding range. Bush puppies are born between April and November, the number will vary between one to two pups in each litter.
Females construct a leaf nest in which this primate bear and care for their offspring. Young bush newborns typically breastfeed for three and a half months, although galagos can take solid food before the end of the first month.
What is their conservation status?
Bushbabies, sometimes known as galagos, are a kind of prosimian that may be found throughout Africa. The species, which is now classified between least concern and critically endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species as the population number varies greatly amongst species.
Galago Monkey Fun Facts
What do galago monkey look like?
Galago monkeys have dense, woolly fur that is silvery gray to brown and fairly long and wavy. Ears are large, with four transverse ridges that may be bent back individually or in unison.
Thicker skin discs on the tips of the fingers and toes aid in gripping tree branches and slippery surfaces. Galagos' tarsus is significantly expanded, reaching one-third the length of the shinbone, allowing these creatures to hop like kangaroos.
Bushbabies are small nocturnal primates that are only found in continental and sub-Saharan Africa. They are galagida family members.
How cute are they?
A group of monkeys looks cute together as galagos have some interesting aspects to their persoanlity and behavior in the forest habitat. Apart from adult galagos, the baby monkeys are so adorable to watch.
How do they communicate?
Alarm, fear, antagonism, and contact calls are all common means of communication among galagos. Tactile communication is very important between mothers and their children, as well as couples. These animals have been observed communicating with one another via vocalizations. The popular name for these creatures comes from the likeness of some of their sounds to a human baby crying.
How big is a galago monkey ?
Mandrill’s are six times bigger than galago monkeys. Greater galago monkeys are 14.5 in (36.8 cm) in terms of length on average.
How fast can a galago monkey run?
The bush babies are extremely fast and agile creatures in their natural habitat. Galagos have got powerful arms and legs which allow them to jump great distances of around 6-7 ft (1.8-2.1 m) in a single jump.
How much does a galago monkey weigh?
Galago monkeys range of weight is 3.35-10.58 oz (0.09-0.29 kg).
What are the male and female names of the species?
There is no name in english for a female galago monkey because monkeys are simply referred to as male and female. It is the major cause in a variety of species.
What would you call a baby galago monkey ?
Baby or young galago monkeys are called infants or pups.
What do they eat?
Galago monkeys feed both during the day and at night but search for food in the forest, only at night. In terms of eating behavior, their main prey is grasshoppers, although this primate species will also consume small birds, fruits, eggs, and flowers.
Galagos primarily consume insects during the rainy season, but during the dry season, galagos exclusively eat the gum that falls off specific trees in acacia-dominated woods.
Are they dangerous?
Since Nycticebus kayan is a nocturnal species, it went undiscovered for a long period. It makes poison from glands at its elbows, which it then consumes. Their bite can be deadly because of anaphylactic shock. The galagos are aggressive towards each other and if kept as a pet should not be kept with other felloe galagos.
Would they make a good pet?
Galagos, like other primates, make poor pets. You'll also have a difficult time finding a captive-bred bunch, and those that are wild-caught for the pet trade endanger the natural populations.
Did you know...
During the day, the galagos sleep. Bush babies curl their ears back to protect themselves when leaping between prickly bushes.
There are at least 20 different types of bush babies, but experts believe there may be up to 40 because not all of them have been identified. Southern Africa, Central Africa, South Africa, East Africa are the regions where these animals are primarily concentrated.
Galagos have massive forward-facing eyeballs that are so big in comparison to their heads that galagos can't move them in their sockets. But this helps them look for food in the forest at night.
In the United States, you can not have bush babies as pets because of restrictions imposed by the government.
Bush babies cry to communicate with each other. Their loud cries enable them to send messages to one another.
Why are galago monkeys called bush babies?
Bush babies are named from their infantile wailing scream, which galagos use to mark territory and communicate with family members. They are very intelligent primates and learn things very quickly in captivity.
What are other names for galago monkeys?
Galago monkeys are sometimes referred to as bushbabies, galagos, or nagapies.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these woolly monkey facts and howler monkey facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable galago monkey coloring pages.