Lophiomys imhausi, maned rats, are usually found in East Africa. Their distribution range extends to Somalia, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Sudan, and Uganda. It prefers to live in upland areas.
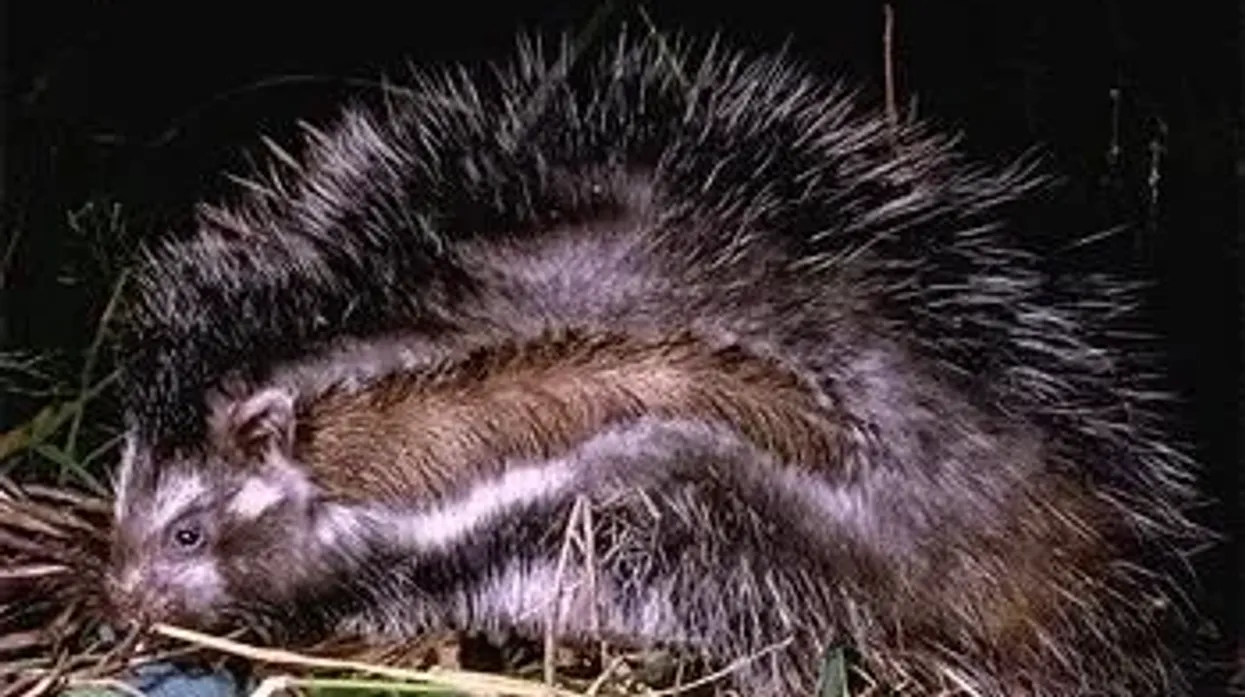
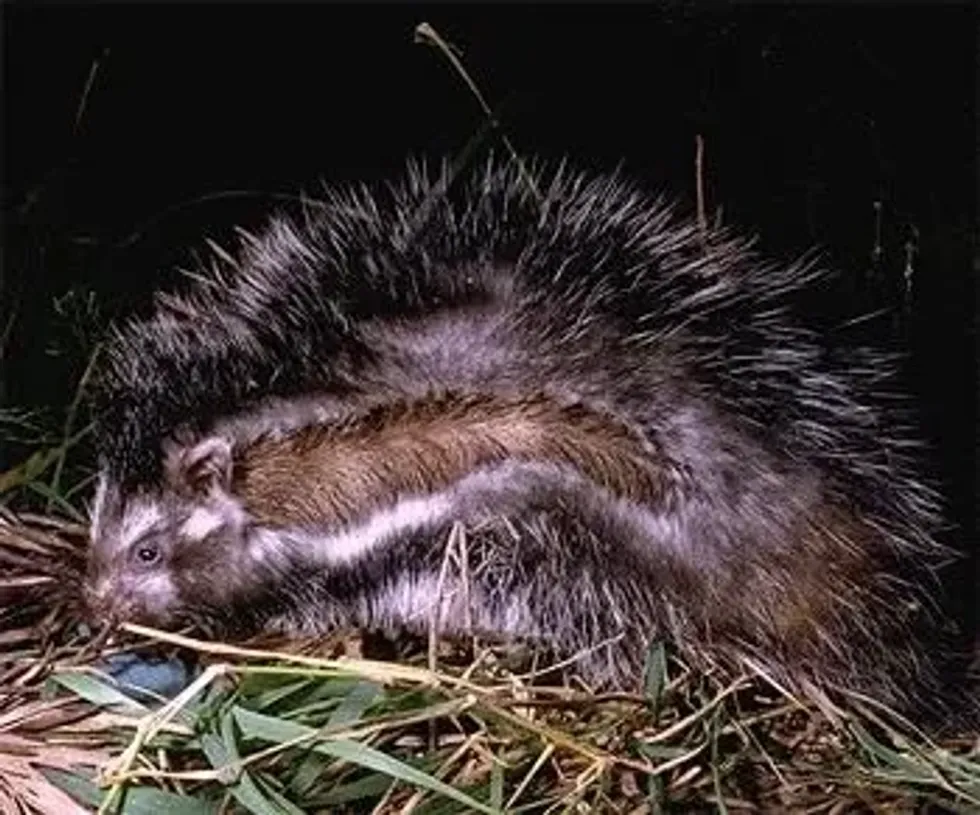
The maned rat's physical appearance is similar to porcupines, but it has white and black stripes on its body. However, the physical features resemble that of a skunk, especially the coat color. It has an unusual skull.
Maned rat adaptations include all kinds of environments, particularly forests. These rats have also adapted to the application of toxins produced by a specific plant known as the poison arrow tree. The maned rat has almost no predators because of its toxicity.
Most of the biology is the same as that of other members of its family. A postdoctoral researcher at Weinstein University considers it as a black box. Agwanda has recorded groups of these rats drawing the poison from the plant, this poison is dangerous to most organisms.
To learn more about other animals, you can also check out yellow rat snake facts and prairie rattlesnake facts.
Maned Rat Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a maned rat?
The maned rat, Lophiomys imhausi, is a small, highly toxic, member of the rodent family.
What class of animal does a Maned rat belong to?
Lophiomys imhausi is an East African animal that belongs to the class Mammalia in phylum Chordata.
How many maned rats are there in the world?
The maned rat's population size has not been estimated yet. Although, these animals are abundantly present in their native regions.
Where does a maned rat live?
Lophiomys imhausi is endemic to Kenya, Somalia, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Sudan, and Uganda. Two researchers, namely Kingdon and Walker, discovered fossils of the maned rat in 1974 and 1975, respectively.
What is a maned rat's habitat?
The maned rat's habitat ranges from the dry forests of South Sudan to the secluded mountain forests of Tanzania. It prefers highland regions.
However, in Ethiopia, it thrives in different habitats from sea level to 10,800 ft (3,300 m). It is also found in the woodlands of Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and Somalia. The natural history of the Lophiomys imhausi has not been completely studied.
It is a nocturnal animal and a great climber. During the daytime, the rodent stays in dens among rocks, in holes of lifeless trees, or inside ravines.
Who do maned rats live with?
Previously, scientists believed that the Lophiomys imhausi was a solitary rodent but it is now known to be slightly sociable. The maned rat generally travels alone but has been reported in pairs or in small groups by scientists.
It may also live alongside other types of rodents and sometimes with hyraxes. Multiple maned rats in the same location purr and groom each other.
How long does a maned rat live?
In captivity, the average lifespan of the Lophiomys imhausi is about eight years.
How do they reproduce?
There is not much information available regarding the reproduction of maned rats. They can give birth to around eight pups or even more. Pups are lightly haired at birth and white and black stripes occur after nine days.
Usually, they open their eyes after the 13th day. The African Maned rat babies' hair is adequately long that the pinnacle can be erectile by day 2o. These animals can move by day 23 and are detached by day 40.
What is their conservation status?
Maned rats are listed as Least Concern in the Red List of Threatened Species of IUCN (The International Union for Conservation of Nature). These animals are abundantly present in a broad range of distribution, but they are threatened by predators such as wild dogs and cats.
Maned Rat Fun Facts
What does the maned rat look like?

The total body length of these animals ranges between 14-21 in (35.5-53.3 cm) from head to tail, and they weigh around 20.8-32.4 oz (590-920 g). Females are slightly larger than males.
This mammal generally has a long body and diminutive limbs. The animal has a coat composed of long, silver and black-tipped hairs over a woolly, thick, white, and gray undercoat (stripes), with the face and limbs being covered in black fur.
A mane of larger, rougher black and white banded hairs stretches from the head to the base of its tail.
This mane is marginalized by a wide, white-bordered strip of hairs. However, limbs possess short black fur.
When the mammal is excited or threatened, the mane erects which results in the expose of the glandular area. The hairs in this region are normal hair but are otherwise fibrous and spongy like honeycomb structures.
L. imhausi is known to voluntarily cover these specialized hairs with poison from the bark of the poison arrow tree. The skull is unusual in this animal.
There are bony projections that stretch over the eye socket and the parietal part is extended. In addition, the skull is strengthened by an extra bone in some regions. These unusual features are believed to be for additional protection against attacks.
L. imhausi has small ears. It has specific feet and hands for feeding as well as climbing (Kingdon and Walker).
How cute are they?
They may look cute and innocent but they are highly poisonous.
How do they communicate?
No information is available about their communication. Although, they do show aggressive behavior when provoked.
How big is a Maned rat?
The maned rat is around 14-21 in (35.5-53.3 cm) long, which is 15 times larger than a rice rat.
How fast can a Maned rat move?
The running speed of this animal is unknown. Although, it is a slow-moving mammal.
How much does a Maned rat weigh?
The weight of L.imhausi lies between 20.8-32.4 oz (590-920 g), which is 10 times bigger and heavier than a shrew.
What are the male and female names of the species?
There are no specific names to describe the male and female maned rat.
What would you call a baby Maned rat?
Like other rats, a baby is generally known as a pup.
What do they eat?
In the wild, the maned rat's diet mainly consists of fruits, leaves, and other plant materials. However, in captivity, it also feeds on cereals, meat, root vegetables, and insects like earthworms, bugs, beetles, and so on. Food is eaten by resting on its haunches and the usage of its forepaws to convey meals to its mouth.
Are they dangerous?
Yes, African crested rats are dangerous. They are highly poisonous but do not produce toxins themselves. They apply a powerful toxin to their specialized hairs.
It is so powerful that just some milligrams can kill a human being. The rats themselves do not produce the poison but withdraw it from a specific plant. The animal is run into human beings at times, who're sometimes escorted by their dogs.
Observers describe that the animal increases its mane when it feels intimidated by dogs. Sadly, a few dogs have died after touching the animal. Those who have recovered have discovered to keep away from the rodent.
Researchers suspect that the poison shields the mammal from dangerous mammalian predators. Their poison is deadly to humans and also to pets. There is no evidence that human hair kills rats.
Would they make a good pet?
No, American crested rats are highly toxic. Keeping a maned rat as a pet is a foolish decision.
Did you know...
The poison of maned rats is cardenolides which are natural cardiac glycosides.
What is the other name of Maned rat?
The maned rat is also known as a crested rodent that looks like a porcupine. However, it is called so because of its black and white banded coat on the mane.
Are Maned rats poisonous?
African crested rats look like cute puffballs but their hair is packed with a lethal poison that can kill an elephant.
In a research paper, National Museums of Kenya researchers and Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute, University of Utah, published that the African crested rat is the only animal known to seize the poison from the bark of the poison arrow tree for chemical defense.
Sara Weinstein, head author, and Smithsonian-Mpala postdoctoral scholar and postdoctoral researcher at the University of Utah, considered this animal as a black box. She said, 'We originally wanted to prove the toxin sequestration behavior was true and along the way found something entirely unknown about social behavior.
Denise Dearing, co-author from the University of Utah said, 'The initial 2011 study observed this behavior in only a single individual. The main goal of our study was to determine how common this exceptional behavior was'.
In the latest study, researchers caught 25 African crested rats. They documented about 1000 hours of their behavior.
As a postdoctoral scholar at the Mpala Research Centre, Weinstein, first looked for rats with digital traps. However, they discovered that they hardly triggered the cameras.
Weinstein then connected through Katrina Nyawira. Together, they contributed months experimenting with traps to seize the elusive rodents.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these black rat facts and firebrat facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable maned rat coloring pages.