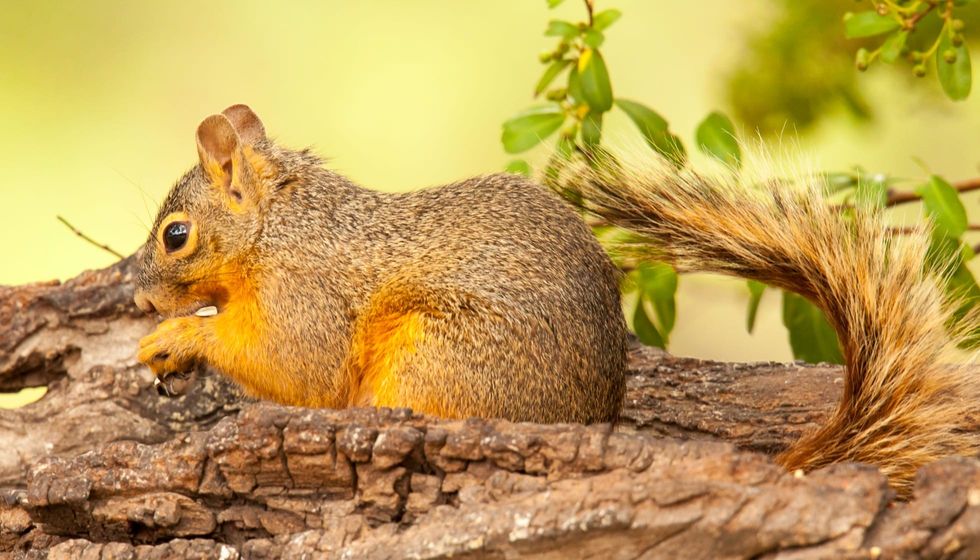
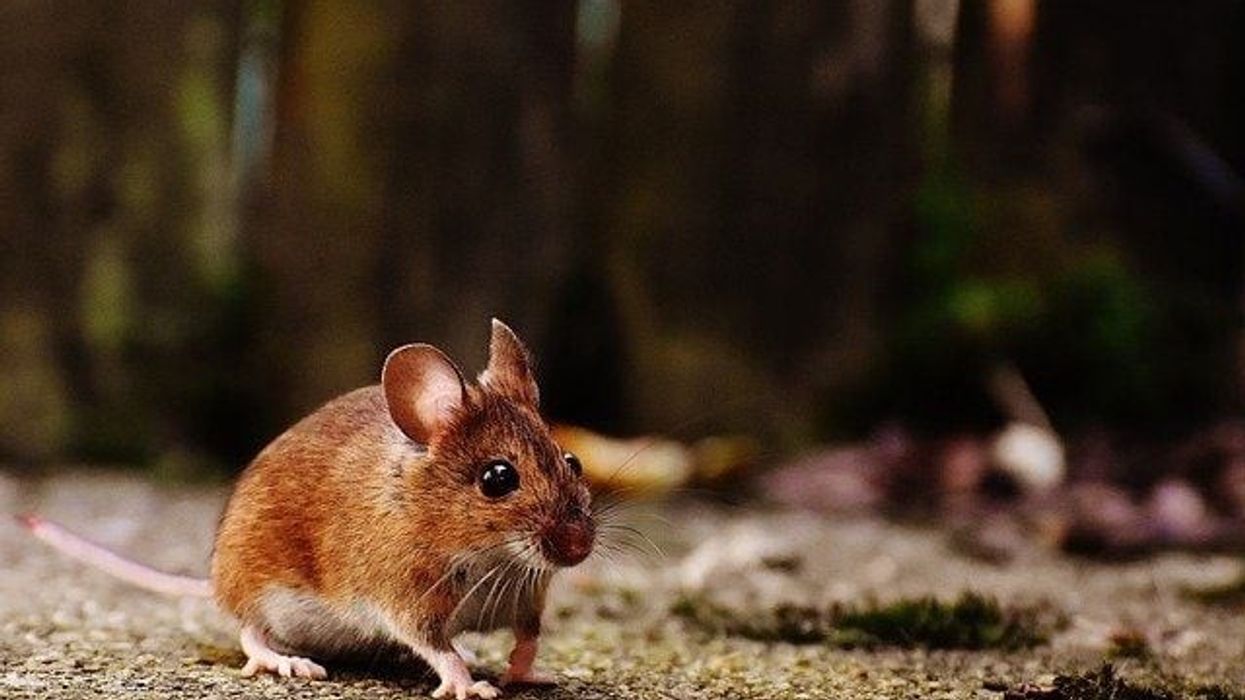
Mexican fox squirrels (scientifically know as Sciurus nayaritensis) is a tree squirrel found throughout the Sierra Madre Occidental of Mexico and the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona, U.S.
They are part of the Sciurus (squirrel) family which is the largest species of climbing squirrel in North America.
Although this fox squirrel is large and primarily on the ground, they are very secretive and tricky to find. Although they mainly have a brown back, a tan to yellow bushy tail, brownish-yellow to reddish sides, the exact size and coloration sciurus depends on their exact geographic variation.
There are three known subspecies for this tree squirrel including the Sciurus nayaritensis nayaritensis (Nayarit fox squirrel), Sciurus nayaritensis chiricahuae (Chiricahua fox squirrel) and (Sciurus nayaritensis apache ) Apache fox squirrel.
Read more interesting facts about the gopher and mongoose to learn more about animals.
Mexican Fox Squirrel Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a Mexican fox squirrel?
The Mexican fox squirrel (Sciurus nayaritensis) is a tree squirrel.
What class of animal does a Mexican fox squirrel belong to?
The Mexican fox squirrel, Sciurus nayaritensis, belongs to the Mammalia class of animals, the order of Rodentia and the genus Sciurus. Of the 28 genus species, this squirrel fits in the subgenus of 14 other squirrel species.
How many Mexican fox squirrels are there in the world?
The exact population size of Mexican fox squirrels across the world is unknown, however, there are three known subspecies that have their own geographic variation.
The reddish Chiricahua fox squirrel, an endemic subspecies, can be found in the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona and as far south as Jalisco Mexico).
The Apache fox squirrel (Sciurus nayaritensis apache) is found in the northern and central portion of the Arizona-Mexico distribution range and this subspecies intermediate in size. The Nayarit fox squirrel, Sciurus nayaritensis nayaritensis, the last subspecies which is much smaller in size and more yellow in color.
As they are very secretive and rarely seen, there is limited information on this species of tree squirrel so the exact distribution numbers remain unknown.
Where does a Mexican fox squirrel live?
The Mexican fox squirrel, Sciurus nayaritensis, can be found in the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona (USA) and in the Sierra Madre Occidental Mountains of Mexico as far south as Jalisco. They have a limited distribution in the Chiricahua mountains and prefer open apache pine-oak to dense trees.
This fox squirrel lives in forests with elevations between 4,900-8,900 feet (1494 to 2713 meters).
What is a Mexican fox squirrel's habitat?
Mexican fox squirrels typically live in forests close to rivers and streams, where ashes, walnuts, sycamores, and large evergreen oaks grow. In the upper Sonoran Zone, these fox squirrels are found in abundance where there are dense concentrations of trees and shrubs in the canyon bottoms. They prefer mature forests that have been maintained by frequent low severity fire.
Who do Mexican fox squirrels live with?
Like most of the genus sciurus, these tree squirrels are generally not gregarious animals, and often fight if they cross paths. To avoid such social interactions, they will use their scent to mark their home range.
For males, their home ranges expand from 30-40 hectares (74-99 acres), and for females, a much smaller 10 to 20 hectares. However, they will interact during breeding season when these ranges collectively shrink with their mating partner.
How long does a Mexican fox squirrel live?
The average lifespan of a Mexican fox squirrel, Sciurus nayaritensis, is still largely inconclusive due to a lack of information on the species. The lifespan of their close relative the red-bellied squirrel, also born in the wild, has lived to 11.5 years in captivity.
How do they reproduce?
There is limited information on the breeding patterns of the Mexican fox squirrel species, however, they are known to reproduce between 1-2 times a year usually in late spring or summer. These tree squirrels will settle in mature seed-producing forests, that will provide suitable nesting locations and an abundance of food.
Mexican fox squirrels nest in dreys built with dry leaves, grass, and twigs.
After the gestation period of roughly 43 days (just over 6 weeks), these fox squirrels typically produce a single litter of one to three offspring. At birth, their young weigh just 0.4 oz (11 g) and are weened for approximately 76 days (just under 11 weeks).
What is their conservation status?
The Mexican fox squirrel is listed as Least Concern. They are not under threat of extinction based on their population and distribution levels.
Mexican Fox Squirrel Fun Facts
What do Mexican fox squirrels look like?
This fox squirrel has a very thick and soft pelage. Although the exact coloration will differ across ranges, seasons, and subspecies, they mainly brown back, brownish-yellow to reddish sides, with a yellow bushy tail.

*Please note that this is an image of a Chiricahua fox squirrel, not a Mexican fox squirrel. If you have an image of a Mexican fox squirrel, please let us know at hello@kidadl.com
How cute are they?
The Mexican fox squirrel is very small with thick soft fur and a bright bush tail, with an aesthetic likeness to a teddy bear making it very cute.
How do they communicate?
Mexican fox squirrels (Sciurus nayaritensis) rarely make noise, and will usually only do so usually due to disturbance. They communicate through both visual and acoustic channels, with some species accompanying their vocalization with a visual signal of flicking their tail. They also have perception channels that are visual, tactile, acoustic, and chemical.
How big is a Mexican fox squirrel?
The average Mexican fox squirrel length is 21 in (53.4 cm) long and with an average weight of 24 oz (680 g). This squirrel is four times the length and 41 times the weight of an African pygmy squirrel (Myosciurus pumilio), the world's smallest squirrel.
How fast can a Mexican fox squirrel run?
The Mexican fox squirrel is very fast. By nature, they are fantastic runners and like other squirrels can run up to speeds of up to 20 mph (32 kph).
How much does a Mexican fox squirrel weigh?
The Mexican fox squirrel weights an average of 24 oz (680 g), which differed slightly between their male and female species. The average weight for a male is 24.13 oz (684 g) and for the female is 24.94 oz (707 g)
What are the male and female names of the species?
The names for male and female Mexican fox squirrels are simply female and male Mexican fox squirrels.
What would you call a baby Mexican fox squirrel?
A baby Mexican fox squirrel is called young.
What do they eat?
The Mexican fox squirrel forages on the ground for their feed which is usually a range of plant and animal food including leaves, wood, bark, grains, seeds, and nuts as well as birds, eggs, insects, and terrestrial worms. Although they are mainly herbivores.
the exact diet of a Sciurus nayaritensis (Mexican fox squirrel), will differ from habitat to habitat and through the different seasons. For Chiricahua fox squirrels, Sciurus nayaritensis chiricahuae, living in the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona, their summer diet is primarily fungi.
The winter months food sources include cypress nuts and berries from mistletoe.
Chiricahua fox squirrels, Sciurus nayaritensis chiricahuae, do not store their food, instead, they hide it under leaf litter and topsoil. Known predatory species include Cooper's hawks and goshawks.
Are they dangerous?
Mexican fox squirrels are not dangerous in nature but more in their ability to carry parasites and viruses, which is their main danger to humans and household pets.
Would they make a good pet?
This fox squirrel would not make a suitable household pet. Although its physically soft features and quiet demeanor is similar to that of traditional domestic pets, these animals are wild and have not been domesticated by humans and they are also carriers of dangerous parasites and viruses.
Did you know...
When hiding from potential predators (like snakes, large raptors, canids, felids and humans), they can remain motionless for more than 45 minutes. Out of all the subspecies, there is the most research on the Chiricahua fox squirrel, as they are endemic to the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona focus studies have been carried out.
Outside of the United States, the squirrel ecology is yet to be thoroughly studied so more research on this secretive species and subspecies is yet to come.
How can you tell the difference between a Mexican fox squirrel from a grey squirrel?
The Eastern gray squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis) is easily distinguishable from Mexican fox squirrels due to their color. The grey squirrel has predominantly grey hair, whilst the latter is predominantly brown.
Is the Mexican fox squirrel endangered?
Although this fox squirrel had been hunted by humans in the past for food and is also hunted as a game species in some areas, it is not considered endangered.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these nutria facts and fox squirrel facts pages.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable Mexican fox squirrel coloring pages.