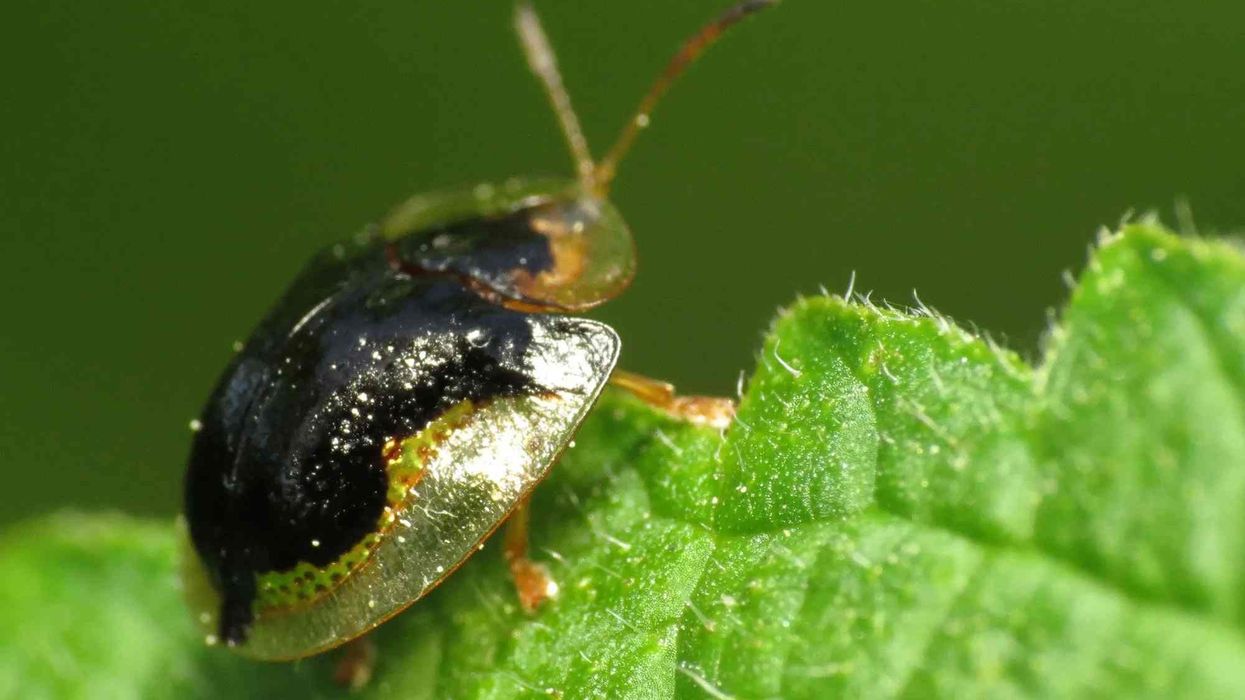
The mottled tortoise beetle (Deloyala guttata) is a tortoise beetle species of the family Chrysomelidae and order Coleoptera. The Deloyala genus consists of 10 recognized tortoise beetle species.
This beetle occupies south, central, and north America. This genus belongs to the Cassidini tribe under the subfamily Cassidinae with leaf beetles.
This tribe is the largest within the subfamily and contains 40 genera of mostly 'tortoise beetles.' Gyllenhal founded the subfamily Cassidinae in his 1813 book, along with the Hispinae subfamily. However, the Cassidinae name is given priority based on the Principal of the First Reviser.
These cassidoids are metallic and colorful with translucent cuticles. The Chrysomelidae consists of more than 37,000 species within over 2,500 genera making this family commonly encountered largest beetle family.
The body of the mottled tortoise beetle consists of mottled patterns with yellow, green, and orange colors. They are named tortoise beetles, as in some of these species, the elytral and pronotal edges extend to the side, covering up their legs.
If these mottled tortoise beetle facts were interesting, make sure to check out rove beetle and tiger beetle facts for more.
Mottled Tortoise Beetle Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a mottled tortoise beetle?
The mottled tortoise beetle (Deloyala guttata) is a species of tortoise and leaf beetles of the order Coleoptera and phylum Arthropoda. Few parasitoids like flies and wasps feed on these beetles. These species are most active in the spring and summer seasons.
What class of animal does a mottled tortoise beetle belong to?
The mottled tortoise beetle (Deloyala guttata) belongs to the insect class of animals
How many mottled tortoise beetles are there in the world?
The exact population number of the mottled tortoise beetle (Deloyala guttata) is not known. However, the population of these species is ample enough for 50 larvae, 50 pupae, and 20 adults to occupy the same six-foot plant.
Where does a mottled tortoise beetle live?
The mottled tortoise beetle (Deloyala guttata) is found in North America, South America, Central America, and the Caribbean. Some places they occupy are New Mexico, Arizona, Texas, and Florida.
What is a mottled tortoise beetle's habitat?
The mottled tortoise beetle's habitat range includes areas with leaf, buds, meadows, fields, parks, and flowers, and stem. They prefer morning glory flowers (Convolvulaceae), milkweed plants, and vines.
Who do mottled tortoise beetles live with?
The mottled tortoise beetle lives in groups.
How long does a mottled tortoise beetle live?
The average lifespan of this beetle species is two to three months.
How do they reproduce?
The adults overwinter and are most active in the spring and summer seasons. The mating and feeding of these species can all take place in the same plant they hatched on. Females lay clusters of eggs each containing 15 eggs under the leaves and then mottled tortoise beetle larvae hide in beetle feces with molted exoskeletons.
What is their conservation status?
The conservation status of the mottles tortoise beetle is Not Evaluated. These species face no threat and their population is abundant across North America.
Mottled Tortoise Beetle Fun Facts
What do mottled tortoise beetles look like?
One of the characteristics of adult beetles is their mottle pattern with yellow, green, and orange colors. They appear like a small and metallic version of their name, with a shell that has glassy edges. The mottled tortoise beetle larva looks like a dark centipede as they are flat and shiny.
How cute are they?
These beetles are colorful and translucent. So, they are considered cute.
How do they communicate?
The adult red lily leaf beetles communicate using pheromones, chemicals, and sound.
How big is a mottled tortoise beetle?
The mottled tortoise beetle is 0.19-0.27 in (5-7 mm) long. These insects are of the same size as the gold-colored golden tortoise beetle. The smallest weevil beetle is smaller than the minimum-sized mottled tortoise beetle.
How fast can mottled tortoise beetles move?
The exact speed of the mottled tortoise beetle is not known.
How much does a mottled tortoise beetle weigh?
The exact weight of the mottled tortoise beetles is not known. However, their relatives, Golden tortoise beetles weigh around 0.11 lb (50 g).
What are the male and female names of the species?
There is no specific name given to the female and male mottled tortoise beetles.
What would you call a baby mottled tortoise beetle?
There is no specific name given to the baby mottled tortoise beetle.
What do they eat?
The mottled tortoise beetles fed on leaf, buds, and flowers, and stem.
Are they dangerous?
No, tortoise beetles are neither dangerous to humans nor any plants because of their small size. So, they are neither a threat nor a pest.
Would they make a good pet?
No, they would not make a good pet. These beetles thrive around plants in garden areas.
Did you know...
Mottled tortoise beetles are active from the month of May to October.
Some more predator species of these beetles are ladybugs and Assassin bugs.
Similar to their relatives, the golden tortoise beetles, mottled tortoise beetles lose their color, which fades into dull brown near the end of their lifespan.
Chrysomelidae family insects are very famous among insect collectors due to their varying colors.
Gold tortoise beetles can change their color when they are disturbed or during mating.
Is the mottled tortoise beetle an invasive species?
The mottled tortoise beetle species is an invasive species and the tortoise beetles are native to Eurasia.
How to get rid of mottled tortoise beetles?
Tortoise beetles are known to feed on the underparts of tomatoes. Although, they do damage the plants completely to kill them. You can hand pick slow-moving adult beetles from plant foliage and drop them into soapy water.
Use gloves or tweezers to pick them. Make sure to search the underparts of leaves. There are products in the market like insecticidal soap products or you make your own spray too.
Spray the solution on water plants to kill these beetles. Make sure to test the solution on a small part of the leaves. You can also use carbaryl spray.
The soap sprays are not toxic to other animals and humans. Although, try not to get this solution into your eyes. Use the carbaryl spray on a calm day and reapply this treatment.
Also, before planting tomatoes use fertilizer and work it into the soil. These species are sometimes beneficial as they feed on nasty weeds. So, to take advantage of this you can spray the tomatoes, which will drive these species to feed on weeds.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these dung beetle facts and blister beetle facts pages.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring on one of our free printable mottled tortoise beet coloring pages.