51 X-Ray Facts: Electrifying Details On Radioactivity Revealed!

X-rays are the electromagnetic radiation originating from electrons that penetrate soft tissues and soft objects with 10 pm-10 nm (100-0.1 Å) of wavelength.
It has a frequency range of 30 PHz to 30 EHz and 124 eV to 124 keV energy valuation, in wavelengths. X-rays usually lie between the UV and gamma rays in the electromagnetic spectrum. Usually, X-rays scans are done in the presence of a physician or medical practitioner to evaluate any irregularities inside the body.
X-rays have other usages as well. X-ray scans can be routine for dental check-ups, mammograms, or prescribed in intervals.
Different tests using the same X-ray technology will vary. For instance, identifying an injured bone will require much less time than a CT scan for brains. These are important points to discuss before scheduling an appointment and you should know the nitty-gritty of the process.
These tests are accommodated in imaging departments of hospitals, medical imaging clinics, and freestanding radiology departments. Even some orthopedic or dental care clinics have their own customized system as well.
In most cases, patients are required to remove clothes when x-rays are used to image certain body parts for better imaging. However, some places can offer hospital gowns or easy-to-change clothing.
Patients will be asked to unfasten any jewelry and remove any eyeglasses, or metal objects.
If you are prescribed to go for an X-ray, where barium contrast dye will be used for identifying digestive issues, then you are going to need to refrain from eating eight hours prior to your test.
If there is any possibility of conducting the test using an enema, then you may have to clean your colon by eating a certain diet or medication.
What is the meaning of X-ray?
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X-radiation within seven weeks of work and got the first-ever Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901. Let us decipher more about X-rays, and learn more about electromagnetic radiation, the electromagnetic spectrum, ultraviolet light, identifying broken bones, X-ray sources, and the human body.
Wilhelm Roentgen named these rays 'X' because these radiations were unknown at that time and according to a mathematical formula, the letter 'X' denotes an unknown element.
An X-ray can be defined in two ways; one by the definition of physics and the other definition given by medical science.
In terms of medicine, an X-ray is defined as a pictorial image of the interior parts of any object or any body. It is commonly used to see the internal parts of a human body after passing the X-rays through it.
The X-rays go through and with the help of colliding different angles, it makes an image that the doctors use to see the broken bones or to do a CT scan.
In physics, an X-ray is defined as an electromagnetic wave in the electromagnetic spectrum of higher energy and short wavelengths like light, which can pass through many opaque objects and ionizing radiation. The radio waves, having the wavelength of X-rays, are 0.01–10 nm (0.1-100 Å). These short-wavelength X-rays penetrate soft tissues and hard solids easily.
Just after the discovery of this X-ray technology, people started to research and use it on different materials as an experiment. By the start of 1896, doctors, physicians, and physicists started to use radio wave technology on patients for CT scans, molecular bonds, cancer cells, and X-ray images.
John Hall-Edwards became the first doctor to make use of radio waves to detect a stuck needle.
The Details Of X-ray Discovery
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen accidentally introduced X-rays while experimenting with Lenard and Crookes tubes to prove if cathode rays can pass through glass. However, he discovered the X-ray and shared his observations in Wurzburg's Physical-Medical Society journal.
The paper was titled 'On a new kind of ray: A preliminary communication'. An X-ray has a higher penetrative ability than microwaves and infrared radiation.
In that trial, Sir Wilhelm was trying to inspect an observation of cathode rays where it was in a Crookes tube that had been wrapped to dodge visible light with black cardboard. There, he used a fluorescent screen, with barium platinocyanide painted on it, and unexpectedly, the tube was emitting a faint green glow.
That means in transition, the ray was penetrating the cardboard (and could possibly penetrate any hard object), which was certainly an unprecedented phenomenon. After two months, the whole thing was placed into the limelight.
Soon after discovering the existence of the X-ray, Roentgen also found that the rays can be used for medical purposes. He took a picture of his wife's hand on a photostimulable plate.
The implementation in the medical industry started with John Hall-Edwards in Birmingham, England. A needle stuck in the hand of his colleague was radiographed by him and later, he stretched the application to include surgical scenarios.
Ivan Romanovich Tarkhanov proved X-rays can influence living function by exposing frogs and insects to radiation. Zoological illustrator James Green started using the technology on fragile specimens.
In the US, Frank Austin got his success in high energy X-ray production with Pului's vacuum tubes. Everyone was trying to capture live X-ray imagery using variations of luminescent screens. Enrico Salvioni and professor McGie made a crypto-scope and skiascope, respectively for this purpose, using barium platinocyanide.
Later, Thomas Edison took part in the quest to discover better imaging techniques and came to the conclusion that calcium tungstate could be an important element. With this understanding, he developed his fluoroscope with this substance capable to capture mass-produced, live imagery and this was established as the most prevalent method to take radiographic images in the medical industry.
One of Edison's aides, Dally, was frequently experimenting with X-rays on his bare hands, which led him to get cancer in both arms. Although he got his hands amputated, he could not be saved and he passed away in 1904.
This phenomenon was unprecedented and made people believe the cons of being exposed to X-rays for a long period of time.
Mihajlo Pupin eased the process of X-ray imaging by using a fluorescent screen. It not only reduced the exposure time to the X-rays but also cut short the time of the entire process from hours to minutes.
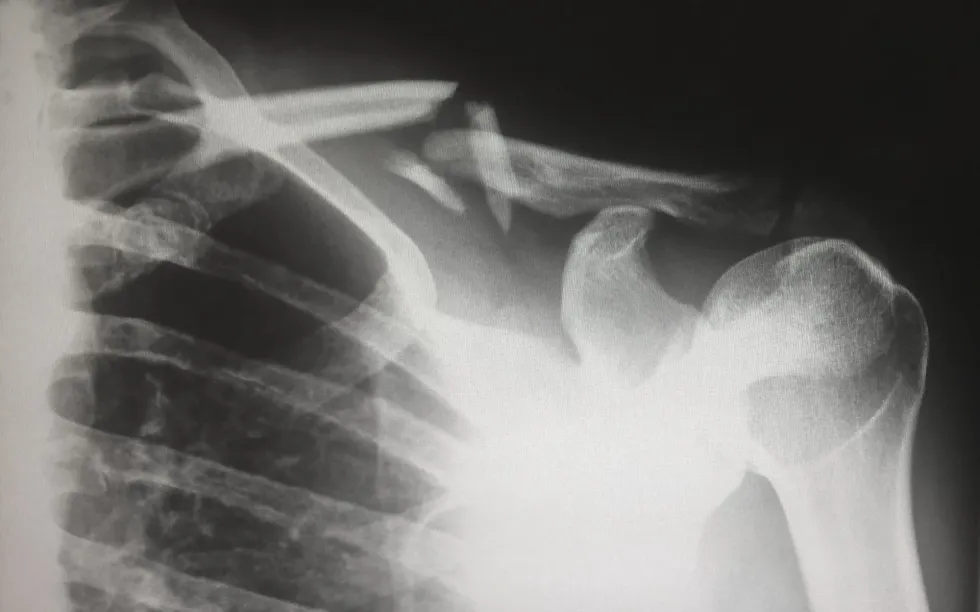
Uses Of X-ray
X-rays were one of the first discoveries for medical examinations.
X-rays are famous nowadays as they are very common examinations prescribed by doctors for imaging internal organs, bones, and soft tissues, and in medical radiography, they are used to find cancer in certain body organs. X-rays can portray internal body components with shadow images on photographic plates.
The technology was primarily deployed to locate any fractures or infections in bones, cavities in teeth, or for basic evaluation of certain parts.
An arthrogram is useful to find arthritis with joint alterations, malignancy in bones, and osteoporosis by measuring bone density. Pneumonia, lung cancer, and tuberculosis can be identified through chest x-rays. Lymphoma in breasts with mammography, heart issues with any conversion in blood flow, and digestive tract issues like kidney stones, and accidentally swallowed objects can also all be identified.
With X-rays, you can be a victim of cancer as a result of EM radiation (electromagnetic radiation), as it is capable of damaging DNA. This, however, depends on the usage, and whether it is a large dose or small dose of radiation on living tissue.
It also depends on the exposure time, which is a little bit longer than usual in fluoroscopy and computed tomography.
According to recommended standards of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the probability of getting cancer from X-rays varies upon fractions of time; more exposure to the radiation makes it plausible to develop cancer in the long run.
Those of a younger age, especially children, are evidently more vulnerable. Women are more prone to get radiation-associated cancer, and certain organs are also more vulnerable.
Patients are seen to encounter breathing difficulty, swelling, allergies like a skin rash or hives, wheezing, asthma, severe dehydration, a decline in blood pressure, constipation, intestinal blockage, perforation, and also convulsion after the usage of contrast medium, barium-sulfate.
If you are injected with iodine, another contrast medium, the symptoms show much later. Your physician or medical assistant will let you know if you are required to have a contrast agent.
Pregnant women are forbidden to take any test that uses a magnetic field if it's not vital, for precautionary reasons.
Reproductive organs usually do not have direct exposure when the machines emit X-rays, however, patients are recommended to protect themselves with a lead apron or collar. In abdominal contrast X-rays, direct exposure during pregnancy can affect your baby according to its gestational age and radiation exposure proportion. Always consult your physician before having a test.
The technology of X- rays also became part of X-ray telescopes that could capture even the minuscule details of the black holes. Using the ray telescopes, one can see the heated matter within black holes.
This helps us to know about black holes in detail through which even light cannot pass! X-ray telescopes also let us observe the milky way and neutron stars.
X-ray telescopes help to observe shorter wavelengths and high-energy matter in outer space. However, the atmospheric layer of the Earth is thick enough to deflect X-rays from the Sun.
X-ray Frequency Range And SI Unit
Photons in higher-energy X-rays are able to ionize atoms, make alterations in molecular bonds and initiate photo-absorption, Rayleigh scattering, and Compton scattering.
A hard X-ray delivers an exorbitant valuation of the photon energy of 10 keV or more, with 0.2-0.1 nm of wavelength. Soft X-rays contain a longer wavelength and have a 600 eV absorption length. Hard X rays are popular in medical radiography and airport security for their penetration capability.
Many variations exist to quantify radiation and here, different facets of X-ray and gamma radiation come into play. Certain implementations require different quantities. In radiation, the conventional unit for exposure is roentgen (R), the SI unit is Coulomb/kg air (C/kg), and the conversion would be 1 C/kg, equaling 3876 R and 1 R equals 258 uC/kg.
The conventional unit of dose goes by rad (R) with SI unit gray (Gy). The conversion is 1 Gy, amounting to 100 rad.
The dose equivalent conventional unit is rem and the SI unit is the sievert (Sv) so the conversion rate looks like 1 Sv equalling 100 rem. Curie (Ci) and becquerel (Bq) are the conventional and SI unit of activity, respectively, and the conversion is 1 mCi equaling 37 mBq.
Did You Know...
During the pre-test, you will be notified to remove your clothes in a private room and put aside your belongings. If contrast dye is required then it will be inserted with injection, enema, intravenous line or you can just swallow it in order to image the internal organs that are about to get diagnosed.
Iodine-based contrast dyes are common when you are tested in arthrogram to identify if you have bursitis or shoulder issues. Barium-based dyes have their use during fluoroscopy.
While using oral barium dye, patients may feel a little bloating or nausea for a brief moment after swallowing the liquid. In the X-ray room, patients have to position their bodies accordingly, so it is important to stay still or the X-ray images will be blurry.
Technicians are recommended to use lead aprons to dodge radiation and stay behind a glass shield while operating. They can set the machine up at different angles.
During mammograms, certain plates are used for compressing the breasts and flattening them while the X-ray image is taken. In a CT scan, you will be inserted into a cylindrical machine.
You will feel nothing but it may seem a little weird if you are claustrophobic. When the tests are done and if any contrast dye got used, you are then required to drink extra fluids to clean your system. With barium-based dye, you may encounter alterations in bowel movement patterns.
If you are a type two diabetic and Glucophage (metformin) substance was used on you then you should stop your daily usual medication for a minimum of 48 hours after the test is conducted. Any ignorance can be responsible for metabolic acidosis which will alter your blood pH.
We Want Your Photos!
More for You
See All
Bachelor of Science specializing in Nautical Science

Ayan BanerjeeBachelor of Science specializing in Nautical Science
Thanks to his degree in nautical science from T.S. Chanakya, IMU Navi Mumbai Campus, Ayan excels at producing high-quality content across a range of genres, with a strong foundation in technical writing. Ayan's contributions as an esteemed member of the editorial board of The Indian Cadet magazine and a valued member of the Chanakya Literary Committee showcase his writing skills. In his free time, Ayan stays active through sports such as badminton, table tennis, trekking, and running marathons. His passion for travel and music also inspire his writing, providing valuable insights.
Master of Arts specializing in History

Sudeshna NagMaster of Arts specializing in History
Having earned a Master's degree in History from the Presidency University in Kolkata, Sudeshna was able to refine these skills and broaden her knowledge base. Not only is she an accomplished fact-checker, but she is also deeply invested in gender research, societal interactions, and mental health. Her professional repertoire also includes experience in translation between Bengali and English content
Disclaimer
1) Kidadl is independent and to make our service free to you the reader we are supported by advertising. We hope you love our recommendations for products and services! What we suggest is selected independently by the Kidadl team. If you purchase using the Buy Now button we may earn a small commission. This does not influence our choices. Prices are correct and items are available at the time the article was published but we cannot guarantee that on the time of reading. Please note that Kidadl is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. We also link to other websites, but are not responsible for their content.
2) At Kidadl, we strive to recommend the very best activities and events. We will always aim to give you accurate information at the date of publication - however, information does change, so it’s important you do your own research, double-check and make the decision that is right for your family. We recognise that not all activities and ideas are appropriate for all children and families or in all circumstances. Our recommended activities are based on age but these are a guide. We recommend that these ideas are used as inspiration, that ideas are undertaken with appropriate adult supervision, and that each adult uses their own discretion and knowledge of their children to consider the safety and suitability. Kidadl cannot accept liability for the execution of these ideas, and parental supervision is advised at all times, as safety is paramount. Anyone using the information provided by Kidadl does so at their own risk and we can not accept liability if things go wrong.
3) Because we are an educational resource, we have quotes and facts about a range of historical and modern figures. We do not endorse the actions of or rhetoric of all the people included in these collections, but we think they are important for growing minds to learn about under the guidance of parents or guardians.