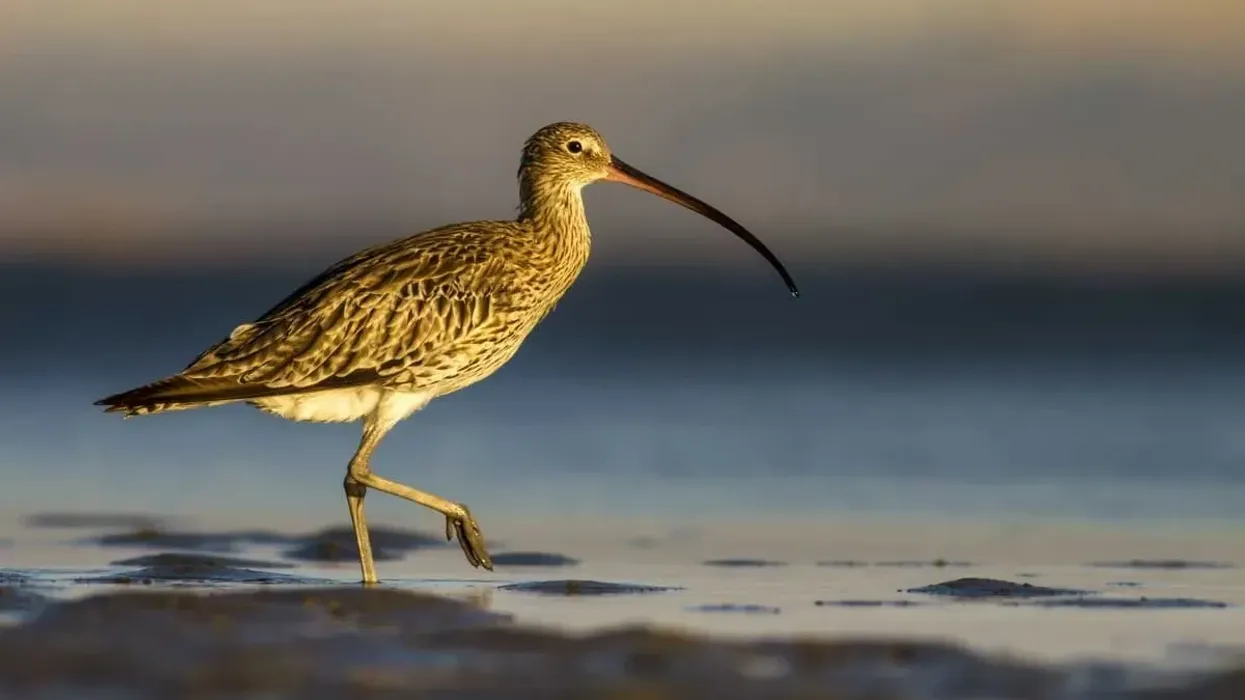
One of the biggest water wader birds in the world is called the Eurasian curlew. The wetlands are home to curlews.
Curlews are migratory birds that spend their winters in southern Europe, Africa, and Asia.
A vagrant species like this can also be seen visiting areas outside of the Eurasian curlew's usual range, such as the Mariana Islands and Nova Scotia.
This bird can be easily identified with its long, prominent beak which is perfect for picking out insects and other smaller meals from marshy wetlands. It also has very long, almost stick-thin legs that allow this bird to wade into the toughest portions of the marshlands, and as a result, have a wider range of search for their food.
If you want to know more about some interesting birds, then look no further than brown falcon facts and saker falcon facts.
Eurasian Curlew Interesting Facts
What type of animal is a Eurasian curlew?
The Eurasian curlew (Numenius arquata) is a type of wader bird.
What class of animal does a Eurasian curlew belong to?
The Eurasian curlew (Numenius arquata) belongs to the class Aves.
How many Eurasian curlews are there in the world?
This species has a big global population of approximately 835,000-1,310,000.
Where does a Eurasian curlew live?
Eurasian curlew (Numenius arquata) lives in the wetlands. The curlew is a migrating bird that spends the winter in southern Europe, Africa, and southern Asia.
In addition, a vagrant species may occasionally go to regions outside of the regular Eurasian curlew range, such as the Mariana Islands and Nova Scotia. It can be seen the whole year in the milder temperatures of Ireland and the United Kingdom throughout the year and its adjacent European coasts.
What is a Eurasian curlew's habitat?
The Eurasian curlew thrives in damp grasslands and marshland and grassy or muddy open habitats in forests, farms, and coastal marshes. It can be found near muddy coasts, estuaries, bays, and muddy edges of inland rivers and lakes, rocky shorelines, and coastal wetlands outside the mating season. Eurasian curlew habitat in moist fields and grassland during migration.
Who do Eurasian curlews live with?
The Eurasian curlew with a longer bill is a sociable bird outside its breeding season. Red-necked phalaropes, wader family birds, in the summer, dwell alone or in small groups, but they can be seen in large flocks or groups during migration to nesting sites and in the cold.
How long does a Eurasian curlew live?
The Eurasian curlew life span is about 10-15 years in the wild.
How do they reproduce?
The breeding season is in the spring, and the producing season is from April to early July for these species. These curlews build their nest entirely in the open, or sedge cover, on a tussock, or in the grass, or among grasses.
A big dip on the ground serves as the nest. The male builds crude scrapes, whereas the female gathers stuff for the nest's lining, usually fine hay, and a few feathers.
The female species lays four darkly marked brownish-olive average-sized eggs. Incubation lasts 27-29 days for both females and males. The silky chicks are a light ochraceous-buff shade over with dark markings at hatching, with a creamy-buff belly. Black is the color of the crown. After hatching, they leave the nest 32-38 days later.
Wader birds like spotted sandpipers are polyandrous. During the breeding season, a female sandpiper mates approximately four males in a single year. Breeding normally takes place between May-August, during the summer months. Female Sandpipers prefer to establish their breeding area before a male sandpiper arrives after selecting a suitable location for their nest.
What is their conservation status?
The conservation status of these species, which belong to the European region, is Near Threatened listed by IUCN Red List.
Eurasian Curlew Fun Facts
What do Eurasian curlews look like?

They have a grayish-brown body, grayish-blue long legs, a white back, and a long curved bill. Males and females have identical appearances, although the mature female's bill is longer than the male's bill.
It's difficult to discern the sex of a solitary Eurasian curlew, let alone many because there's so much variance; nevertheless, identifying the female and male of a paired couple apart is generally possible. Their eyes are deep brown.
How cute are they?
These curlews are beautiful and appealing birds with their long curved bill.
How do they communicate?
The Eurasian curlew has a strong, unmistakable 'curloo oo' or 'cour-lee' call that may be heard both during the breeding season and during the winter. Whenever the bird is startled, the call grows louder and noisy.
It makes a loud, high-pitched sound when it is enthusiastic. Long, consonant, flowing, bubbling syllables can be heard during courtship displays and in the winter. A melodious, ascending whistle serves as the flight call.
How big is a Eurasian curlew?
The Eurasian curlew size is between 20–24 in (50.8–60.9 cm). Another bird of wader group, the solitary sandpiper, measures around 7.4-9 in(18.7-22.8 cm). These species of sandpipe are much smaller than curlews birds.
How fast can a Eurasian curlew fly?
Eurasian curlew flight range is between 1.9-21.5 mph (3.2-34.7 kph).
How much does a Eurasian curlew weigh?
The weight range of Eurasian curlew species is about 14-48 oz (396.8–1360.7 g).
What are the male and female names of the species?
There is no special name for male and female birds of Eurasian curlews.
What would you call a baby Eurasian curlew?
Baby long curved bill curlews have no specific name.
What do they eat?
The Eurasian long-billed curlew feeds mostly on arthropods, annelids, crustaceans, mollusks, berries, and seeds throughout the year. In addition, however, it has been known to eat animals such as amphibians, lizards, small fish, young birds (including eggs), and small rodents.
In the intertidal zone, it scavenges in shallow or deep water. It eats damp or mud earth by jabbing, pecking, and deep probing. Because female and male bills are of different lengths, they graze in distinct places. The female eats on intertidal flats, whilst the male eats developed grassland.
Are they dangerous?
These long-billed curlew of Europe are not dangerous.
Would they make a good pet?
These curlews are considered Near Threatened birds by IUCN Red List.
Did you know...
The English term 'curlew' is derived from the call of the Eurasian curlew, but it is possible that it was inspired by the French Word corliu, 'messenger,' from courir, 'to run'.
What is the difference between a curlew and a whimbrel?
Whimbrels are smaller than curlews in size. The bill of a whimbrel bird is smaller than that of a curlew, and it bends more abruptly at the tip. It has a more prominent head pattern than the curlew, with two dark stripes divided by a smaller, pale middle stripe.
Far eastern curlew vs Eurasian curlew
Eurasian curlews are significantly shorter and have a smaller bill than far eastern curlews when perched; their underparts are whiter with a white background color. Their sides possess thin dark stripes with no evidence of barring.
In-flight, Eurasian curlew can be distinguished from far eastern curlew by its whitish rump, back, upper tail coverts (brown color in the far eastern curlew), and white color underwing coverts.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly animal facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these eared dove facts and night heron facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable sparrow coloring pages.