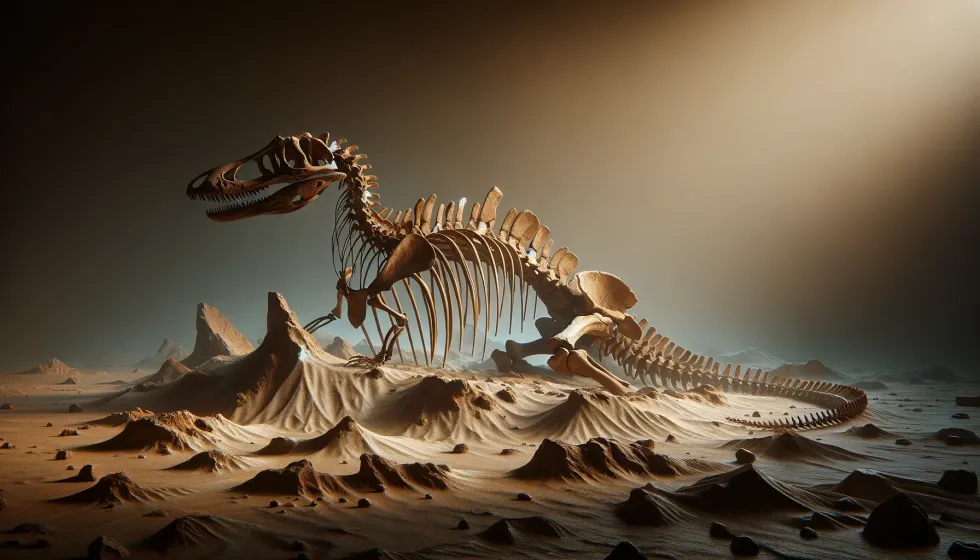
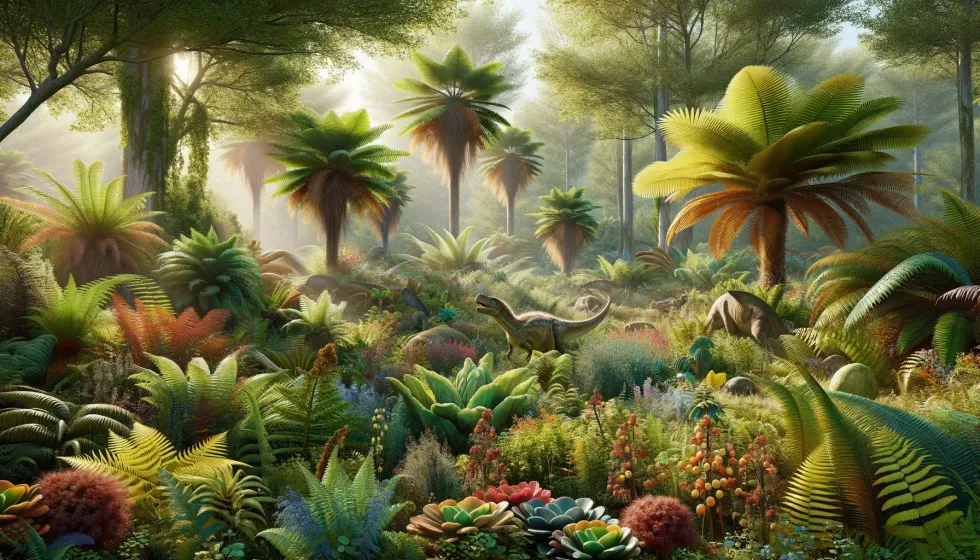
Discovered from the ancient layers of the Morrison Formation, the Dryosaurus fossils have offered a treasure trove of insight into this former herbivorous creature's existence. Scholars have tirelessly solved these prehistoric puzzles, fleshing out a narrative of a dinosaur whose existence was tailored to the lush floodplains of the Late Jurassic (163.5-145 million years ago) landscape.
Adapted to a life of grazing, the Dryosaurus was equipped with specialized teeth ideally shaped for a diet consisting primarily of ground-level flora.
These discoveries have characterized the 'oak lizard' as a dinosaur of intimidating agility and remarkable balance and as an ancient inhabitant who once played an integral role in the dynamic ecosystems of what is now the western United States.
From the tough skeletons held in the storied halls of the Carnegie Museum of Natural History to the juvenile skulls safeguarded within the Dinosaur National Monument, each fossil tells a story of adaptation, survival, and the many ways in which the Dryosaurus navigated a world packed with various dinosaurs and ever-present challenges.
Dryosaurus Interesting Facts
How do you pronounce 'Dryosaurus '?
Dryosaurus is pronounced as 'DRY-oh-SAW-rus'.
What type of dinosaur was a Dryosaurus?

Dryosaurus was an ornithopod dinosaur recognized for its agility and bipedal movement.
In which geological period did the Dryosaurus roam the Earth?
Dryosaurus lived around 155-145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic Period (163.5-145 million years ago), a time marked by the reign of various dinosaurs.
When did the Dryosaurus become extinct?
Dryosaurus became extinct approximately 145 million years ago at the end of the Jurassic Period (201-145 million years ago).
Where did Dryosaurus live?
These dinosaurs lived in what is now known as the western United States, particularly in states like Colorado, Wyoming, and Utah, where their fossils were discovered.
What was the Dryosaurus's habitat?
 Dryosaurus Interesting Facts
Dryosaurus Interesting FactsDryosaurus occupied forest areas nestled within vast floodplains, feeding on ground-level plants.
Who did the Dryosaurus live with?
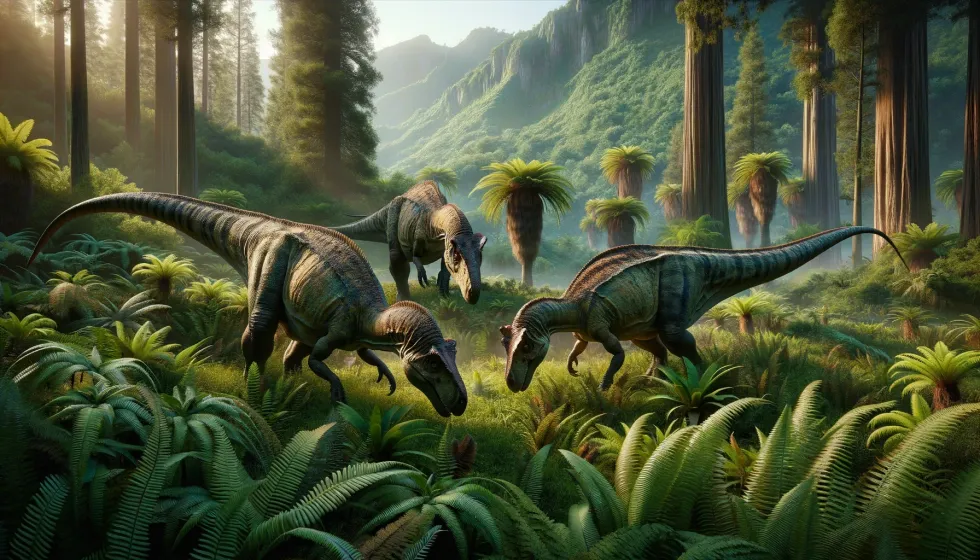
In the Late Jurassic's Morrison Formation, a hotspot of prehistoric life, Dryosaurus shared its environment with an impressive roster of peers. The territory teemed with the armored Stegosaurus and massive sauropods such as Apatosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Camarasaurus, and Diplodocus.
These vast creatures lived where strong hunters like Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus roamed, creating a lively environment where Dryosaurus went about its day-to-day life.
How long did a Dryosaurus live?
The lifespan of Dryosaurus is unknown, but they experienced different stages of growth, as indicated by the juvenile skull and adult specimens found.
How did the Dryosaurus reproduce?

Like other dinosaurs, Dryosaurus reproduced through egg-laying.
Dryosaurus Fun Facts
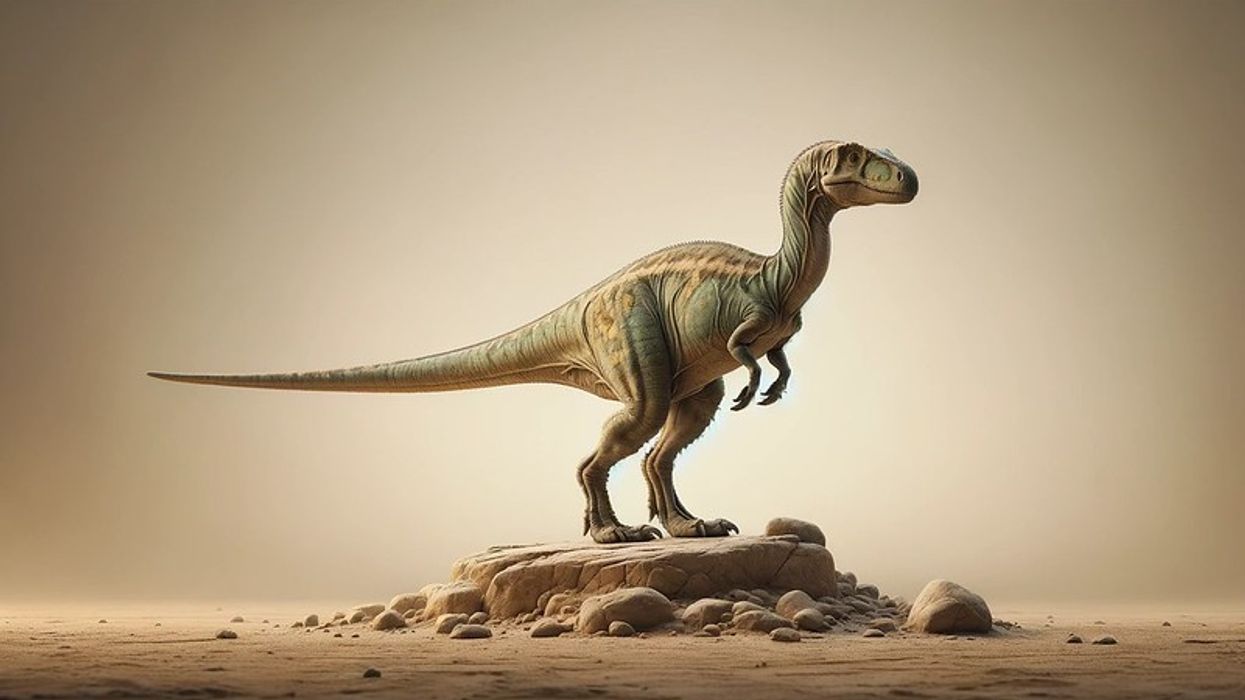
What did the Dryosaurus look like?
A typical Dryosaurus was a small, fast-moving herbivorous dinosaur with strong legs for escaping predators, a stiff tail to retain balance, and cheek teeth adapted for a plant-based diet.
How many bones did a Dryosaurus have?

The exact number of bones in the Dryosaurus is not known.
How did the Dryosaurus communicate?
Dryosaurus may have communicated using visual cues or vocalizations similar to modern-day reptiles and birds, although the exact means of communication are uncertain.
How big was the Dryosaurus?
An adult Dryosaurus could reach up to 9.8 ft (3 m) in length and stood approximately 5-6 ft (1.5-2 m) tall at the hip.
How fast could a Dryosaurus move?
The shape of Dryosaurus' legs suggests that it could move quickly, although the precise speed is unknown.
How much did a Dryosaurus weigh?
It's estimated that a grown-up Dryosaurus might have weighed about 220 lb (100 kg).
What were the male and female names of the Dryosaurus?
There are no separate names. Males and females of the species were both referred to as Dryosaurus.
What would you call a baby Dryosaurus?
A baby Dryosaurus would be called a hatchling or juvenile.
How aggressive was the Dryosaurus?

The Dryosaurus ate plants and likely wasn't a fighter. It mostly stayed calm unless it had to protect itself from predators or get the necessary food and water.
Did you know...
The New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin and institutions like the Carnegie Museum have published findings on Dryosaurus, providing examples of its anatomy and ecology.
The Dryosaurus, which means 'tree lizard' in Greek, lived in North America's swampy areas and thick forests during the Jurassic period. This plant-eating dinosaur stood on two legs and was good at quickly finding food, showing it could easily live in the lush greenery of its time.
FAQs
What kind of dinosaur is a Dryosaurus?
The Dryosaurus is classified as an ornithopod dinosaur, a group of herbivorous species known for their bipedal stance and ability to walk on two legs. These dinosaurs are part of the larger clade Ornithischia, characterized by their bird-like hips and beak-like mouths for cropping vegetation.
Dryosaurus, in particular, was a relatively small ornithopod. Its strong hindlimbs for swift movement and long tail provided balance, enhancing its ability to swiftly navigate through the terrain of its Late Jurassic habitat.
Did Dryosaurus live with Allosaurus?
Yes, the Dryosaurus likely shared its habitat with the Allosaurus. Both species lived during the Late Jurassic Period. Their remains have been discovered in the Morrison Formation, an extensive sedimentary rock layer covering parts of the western United States, suggesting they coexisted in the same regions.
The Allosaurus, a big hunter, might have hunted the Dryosaurus, which only ate plants. Since the fossils of both dinosaurs were found together, they likely lived in the same area, but they ate different things, one meat, and the other plants.
What was the behavior of a Dryosaurus?
The behavior of Dryosaurus, while not fully understood, can be deduced from its physical characteristics and the environments in which it lived. As an herbivorous ornithopod, Dryosaurus likely spent much of its time searching for plants and vegetation.
Its strong legs suggest it was well-adapted for fast movement, which could imply a wandering lifestyle, potentially moving in groups to different feeding areas as seasons changed.
The stiff tail and agile build of the Dryosaurus indicate it was capable of quick moves, which would have been essential for avoiding predators like Allosaurus. The teeth in Dryosaurus' cheeks show it ate plants from the ground. So, it probably munched on certain kinds of plants, carefully picking out its favorites.
Although direct evidence of social behavior is lacking, the discovery of multiple specimens near each other could hint at potential herd behavior or at least some level of social interaction. This behavior would align with other ornithopods, often believed to have had complex social structures.
But because there aren't enough fossils showing groups of Dryosaurus together, scientists aren't entirely sure how they acted.
What era did the Dryosaurus live in?
The Dryosaurus lived during the Late Jurassic Era, from approximately 163.5-145 million years ago. This period is known for its diverse dinosaur species and significant evolutionary plant and animal life developments. The existence of Dryosaurus has been mainly linked to the latter part of the Late Jurassic, evidenced by fossil discoveries that have been dated to this timeframe.
What kind of environment did the Dryosaurus prefer?
The Dryosaurus is believed to have preferred environments with plenty of vegetation, such as forested areas and rich floodplains. Evidence from fossil sites in the Morrison Formation indicates that this dinosaur lived in regions that supported various plant life essential for its herbivorous diet.
What evidence is available of the Dryosaurus's existence?
The existence of Dryosaurus is confirmed through various fossils discovered primarily in North America. These fossils include partial skeletons, bones, and teeth. Specimens recovered from the Morrison Formation have been critical in understanding this dinosaur's physical characteristics and potential behaviors.
How did the Dryosaurus protect itself from predators?
As a smaller herbivorous dinosaur, the Dryosaurus's primary defense against predators was likely its agility and speed. Its powerful legs would have enabled quick escapes from danger. Additionally, living in groups or herds might have provided protective benefits through increased vigilance and communal defense strategies.
How do paleontologists study Dryosaurus fossils?
Scientists who study old bones, called paleontologists, dig up Dryosaurus fossils very gently and then look at them closely in labs.
They use different ways, like comparing body parts to other animals, taking X-ray pictures, and looking at the bones under a microscope, to learn what the dinosaur looked like, how it grew, what it ate, and how it lived.
The dinosaur's teeth are beneficial for figuring out its diet, and looking at bone details can tell how fast it grew and other life details.
What adaptations did Dryosaurus have for its herbivorous lifestyle?
Dryosaurus was built just right for eating plants. It had a mouth shaped like a beak to clip plants easily and flat teeth on the sides for chewing up leaves and twigs.
Did the Dryosaurus display any parental care?
While direct evidence of parental care in Dryosaurus is lacking, other ornithopod dinosaurs have shown signs of such behavior. This leads scientists to guess that Dryosaurus may have also shown some care for their young. This could have included protecting nests or assisting newly hatched juveniles.
How does the Dryosaurus compare to other ornithopods of its time?
Dryosaurus was smaller than some similar dinosaurs, like Iguanodon. It stood on two legs and ate plants just like them. But because it wasn't that big, it was probably quicker and had clever ways to stay safe and find food.
What was the geographical range of Dryosaurus during the late Jurassic?
Dryosaurus mostly lived in what is now the western part of the United States. Scientists have found their fossils in places from the flat lands of Wyoming to the rocky areas of Colorado and Utah.
How did the changing climate of the late Jurassic affect Dryosaurus?
The changing climate of the Late Jurassic, marked by fluctuations in sea levels and volcanic activity, could have influenced the migration patterns and available habitats for Dryosaurus. As herbivores, their diet and survival would have been closely tied to the plant life that thrived in their ecosystems, which were sensitive to climate changes.
What other dinosaurs coexisted alongside Dryosaurus?
Apart from predators like Allosaurus, other dinosaurs that likely coexisted alongside Dryosaurus include the long-necked sauropods like Apatosaurus and Diplodocus, as well as armored dinosaurs like Stegosaurus. These species shared the same environment and would have been part of a balanced ecosystem.
What technologies are used to study Dryosaurus fossils that weren't available in the past?
Thanks to new tech tools, like 3D scanning and special types of imaging, scientists can study Dryosaurus fossils without breaking them. These cool methods give a really clear picture of what the dinosaur looked like and how it lived, even showing parts like muscles and the world it lived in, which were hard to know about before.
Dryosaurus is a remarkable chapter in the story of the Late Jurassic Period. With its unique characteristics as an ornithopod dinosaur, from its agile movement and herbivorous diet to its survival among the giants of its time, the 'oak lizard' leaves a legacy grounded in the diverse ecosystem of ancient North America.
The ongoing discovery and study of Dryosaurus fossils continue to illuminate the evolutionary narrative of these fascinating creatures.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web




 Dryosaurus Interesting Facts
Dryosaurus Interesting Facts