Dyoplosaurus is an extinct genus of armor-bodied dinosaurs within the family Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. This genus belonged to the Late Cretaceous time period's lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation in the most recent Campanian stage around 76.5 million years ago.
They occupied Alberta in modern-day Canada. The genus Dyoplosaurus means 'double-armored lizard.'
There is only one species known of this genus called Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus as per a study on redescription by Arbour, Sissons, and Burns. Based on the ROM 784 holotype material, William Parks named this genus in 1924.
This holotype material is a partial skeleton of the Dyoplosaurus with lower jaws and skulls. The material of this specimen was collected from a 32.8 ft ( 10 m ) bottom in the Dinosaur Park Formation, close to the currently named Red Deer River, Alberta, in Canada.
It was proposed by Walter Coombs in 1971 that Dyoplosaurus was the Euoplocephalus tutus' junior synonymy. However, the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology published a redescription of this genus that claimed it to be a valid taxon.
The Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus (Parks, 1924) type specimen measured around 13-15 ft (4-4.5 m) in length. There are 11 subgroups of Ankylosauridae.
If you enjoyed reading these fun facts about the Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus, then you may also read more facts about Austroraptor and Ludodactylus on Kidadl.
Dyoplosaurus Interesting Facts
How do you pronounce 'Dyoplosaurus'?
The pronunciation of the genus Dyoplosaurus is 'Die-op-loe-sore-us.'
What type of dinosaur was a Dyoplosaurus?
The Dyoplosaurus genus is classified within the order Ornithischia and phylum Chordata. The Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus (Parks, 1924) has an armored body with a tail club like other ankylosaurid dinosaurs.
This dinosaur is ground-dwelling and quadrupedal with a herbivorous diet. Before the redescription in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology identified Dyoplosaurus as a valid taxon, Euoplocephalus, and Dyoplosaurus were considered one and the same, and specimens of Dyoplosaurus were identified as Euoplocephalus tutus.
The Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology mentioned that Dyoplosaurus was identified as a synonymy because of the fragmentary nature of both the Euoplocephalus tutus and Dyoplosaurus' holotype material.
The current cladogram is known due to the redescription and a phylogenetic analysis conducted on Ankylosaurinae in 2015 by Arbour and Currie. This holotype with skull and jaws is one of the most complete armor dinosaur species of Ankylosauridae.
In which geological period did the Dyoplosaurus roam the earth?
Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus (Parks, 1924) roamed the Earth in the Late Cretaceous time period in history in the Campanian stage around 76.5 million years ago.
When did the Dyoplosaurus become extinct?
Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus (Parks, 1924) probably became extinct during the extinction event in the Cretaceous-Paleogene time period around 66 million years ago.
Where did a Dyoplosaurus live?
These specimens of the Late Cretaceous were spread across present-day North America in Alberta, Canada.
What was a Dyoplosaurus's habitat?
The Dyoplosaurus' habitat included terrestrial woodlands.
Who did a Dyoplosaurus live with?
These species of genus Dyoplosaurus (from the Late Cretaceous) probably lived with their own kind in a group, like all other dinosaurs.
How long did a Dyoplosaurus live?
The maximum, or even average, life expectancy of these dinosaurs of the Late Cretaceous period is not known.
How did they reproduce?
The reproduction of these species of the Late Cretaceous period was oviparous. However, data on the breeding, incubation period, and parental care of these dinosaurs is not available.
Dyoplosaurus Fun Facts
What did a Dyoplosaurus look like?
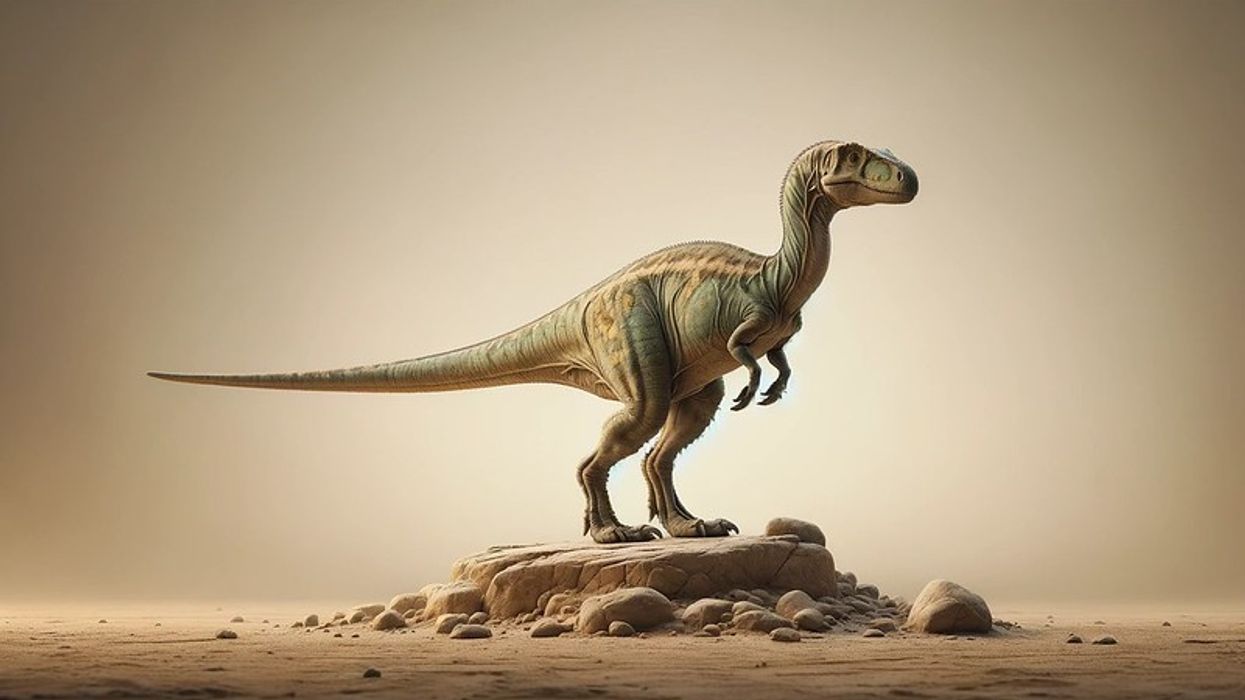
 We've been unable to source an image of a Dyoplosaurus and have used an image of a Talarurus instead. If you are able to provide us with a royalty-free image of a Dyoplosaurus, we would be happy to credit you. Please contact us at hello@kidadl.com.
We've been unable to source an image of a Dyoplosaurus and have used an image of a Talarurus instead. If you are able to provide us with a royalty-free image of a Dyoplosaurus, we would be happy to credit you. Please contact us at hello@kidadl.com. The description and redescription of these dinosaurs of the Dyoplosaurus genus were done based on a not-so-complete holotype. These species were quadrupedal and ground-dwelling dinosaurs.
They had an armored body and a tail club (a bony fragment at the end of their tail). It is mentioned in a study that there were many armor plates merged together in the tail club. Also, this tail club is narrower and smaller than any other ankylosaurid's tail.
How many bones did a Dyoplosaurus have?
The total number of bones in the skeleton of these species is not yet known. The Dyoplosaurus fossil remains were partial fragmentary skeletons with lower jaws and skulls. The fossils that were found of the Euoplocephalus were teeth, 15 skulls, and an almost complete skeleton with attached armor.
How did they communicate?
The mode of communication of these ankylosaurids of the Dyoplosaurus genus is not known. However, they might have communicated through body language, calls, and songs.
How big was a Dyoplosaurus?
These species measured around 13-15 ft (4-4.5 m) in length as per a study by Arbour and Mallon. They measured 5.8 ft (1.7 m) wide. The Dyoplosaurus skull measured around 14 in (35 cm). The Euoplocephalus (E. tutus) species were a little longer than these species, measuring about 20 ft (6m).
How fast could a Dyoplosaurus move?
The running speed of ankylosaurids is not yet known.
How much did a Dyoplosaurus weigh?
The weight of these species is around 2,000 lb (907.1 kg). Their relatives, E. tutus, were two times heavier than these species.
What were the male and female names of the species?
There is no specific name given to these female or male dinosaurs.
What would you call a baby Dyoplosaurus?
There is no specific name given to these baby dinosaurs.
What did they eat?
Dyoplosaurus' diet was herbivorous. They might have fed on plants and leaves.
How aggressive were they?
The aggressiveness of these dinosaurs is not known. However, they might have shown aggression while defending territories.
Did you know...
The first fossil within the Euoplocephalus genus was recovered in Alberta in 1897. The only named species of Euoplocephalus is E. tutus.
This group was previously named Stereocephalus in 1902 but this name was already given to an insect group. The first specimen of Euoplocephalus was discovered by Lawrence Morris Lambe, a Canadian paleontologist in 1897 in the Dinosaur Provincial Park, Red Deer River Valley in Alberta.
The presence of the tail club in Ankylosaurids has always been believed to have helped them defend themselves. Few other opinions are that the tail club was used for display or combat.
However, some researchers think otherwise, stating that there are no modern tetrapods that use tails for any such purpose. The few other groups in this family are Minmi, Shamosaurus, and Gobisaurus.
Pinacosaurus vs Dyoplosaurus: both belong to the same subfamily. Pinacosaurus means 'plank lizard' and Dyoplosaurus means 'double-armored dinosaur.'
Pinacosaurus was medium-sized measuring up to 20 ft (5 m) and Dyoplosaurus was 13-15 ft (4-4.5 m) in length. Both the species differ in the skull armor details. Also, the Pinacosaurus have low-slung and flat and not heavily built like the Dyoplosaurus species.
The skull of an adult Pinacosaurus was longer than wide and had fused mass instead of distinct tiles on their upper snout armor. It was also noted by Arbour that the species with Pinacosaurus also had few distinguishing traits.
What was unique about the Dyoplosaurus?
Dyoplosaurus can be distinguished from the other ankylosaurs by their hips and vertebrae, particularly the tail making these species distinct from the hips back. This holotype with skull and jaws is one of the most complete armor dinosaur species of Ankylosauridae
How did the Dyoplosaurus get its name?
Dyoplosaurus was given the name based on the ROM 784 holotype material collected from Dinosaur Park Formation. They were given this name because of their heavily armored body, translating Dyoplosaurus to 'double-armored dinosaur.'
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly dinosaur facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these Metriorhynchus facts and Chungkingosaurus facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable Dyoplosaurus coloring pages.