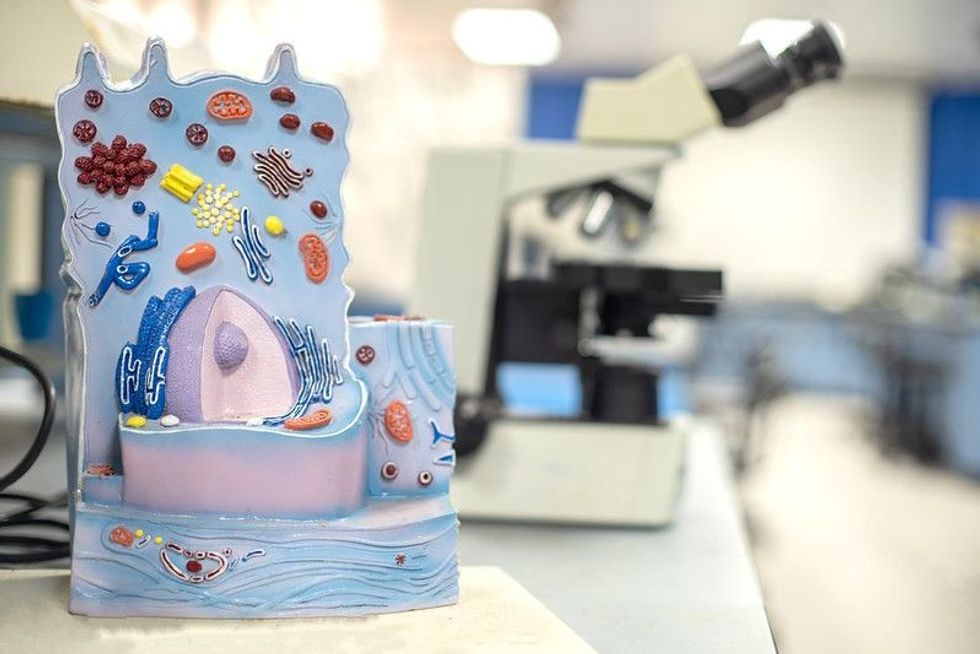
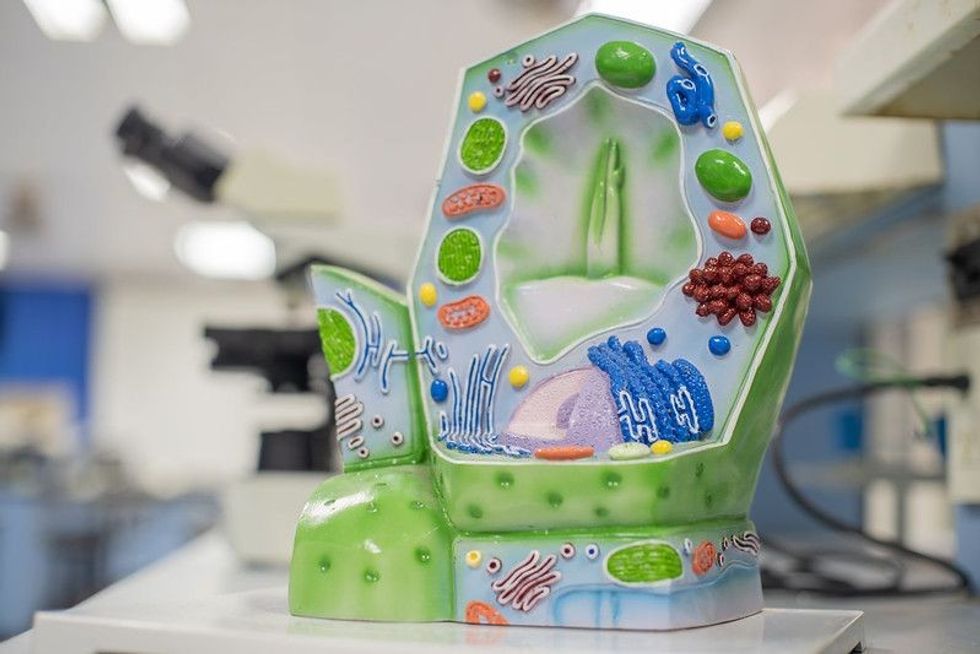
15 Organelle Facts: Learn About These Structures Inside Cells
We Want Your Photos!
More for You
Sources
https://www.encyclopedia.com/plants-and-animals/zoology-and-veterinary-medicine/zoology-general/organelle#:~:text=Organelles also function in transportalso have organelles called vacuoles.
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/organelles/#:~:text=Organelles are specialized structures that perform various jobs inside cellsto keep a cell alive.
https://www.thoughtco.com/facts-about-cells-373372
https://lisbdnet.com/what-are-the-organelles-only-found-in-plants/#:~:text=The two organelles found onlyare chloroplasts and central vacuoles.
See All
Disclaimer
1) Kidadl is independent and to make our service free to you the reader we are supported by advertising. We hope you love our recommendations for products and services! What we suggest is selected independently by the Kidadl team. If you purchase using the Buy Now button we may earn a small commission. This does not influence our choices. Prices are correct and items are available at the time the article was published but we cannot guarantee that on the time of reading. Please note that Kidadl is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. We also link to other websites, but are not responsible for their content.
2) At Kidadl, we strive to recommend the very best activities and events. We will always aim to give you accurate information at the date of publication - however, information does change, so it’s important you do your own research, double-check and make the decision that is right for your family. We recognise that not all activities and ideas are appropriate for all children and families or in all circumstances. Our recommended activities are based on age but these are a guide. We recommend that these ideas are used as inspiration, that ideas are undertaken with appropriate adult supervision, and that each adult uses their own discretion and knowledge of their children to consider the safety and suitability. Kidadl cannot accept liability for the execution of these ideas, and parental supervision is advised at all times, as safety is paramount. Anyone using the information provided by Kidadl does so at their own risk and we can not accept liability if things go wrong.
3) Because we are an educational resource, we have quotes and facts about a range of historical and modern figures. We do not endorse the actions of or rhetoric of all the people included in these collections, but we think they are important for growing minds to learn about under the guidance of parents or guardians.