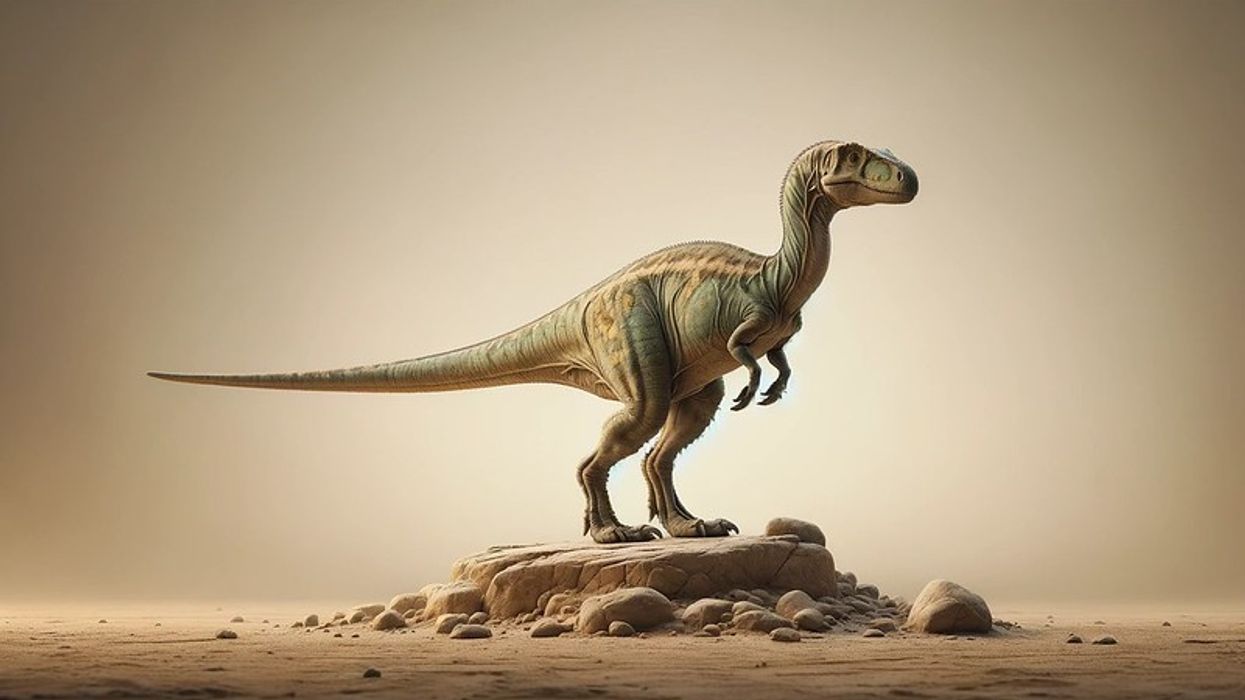
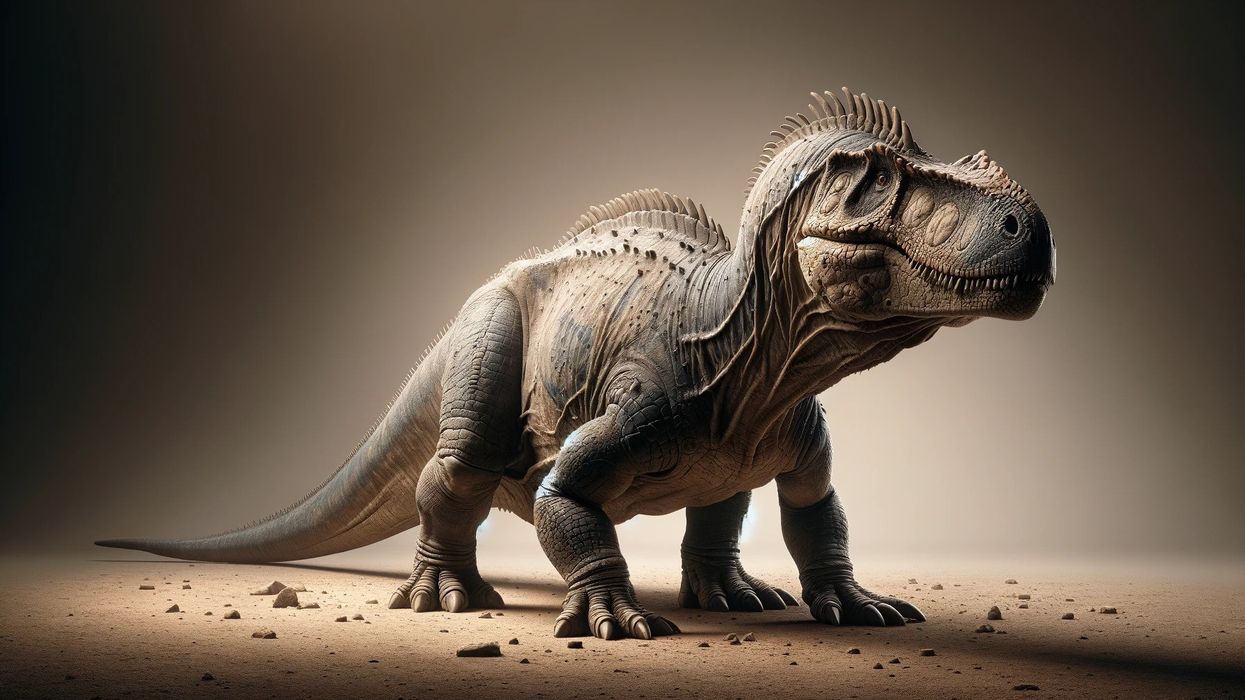
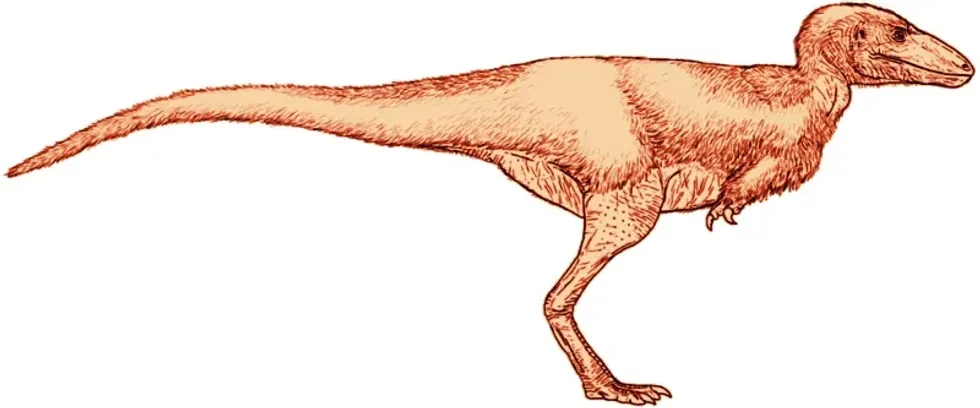
Alectrosaurus is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaurs of the superfamily Tyrannosauroidea. The dinosaur of this genus lived in the Late Cretaceous period of Asia around 83-74 million years ago, which is currently the Iren Dabasu Formation.
The Greek term Alectrosaurus translates to 'unmarried lizard' or 'alone lizard.' This dinosaur was a well-built ground-dwelling bipedal related to the larger and more advanced Tyrannosaurus.
However, the advanced species of Tyrannosaurids did not run very fast while pursuing their prey like the Alectrosaurus. Walter W. Granger, the chief paleontologist of the American Museum of Natural History, led an Asiatic expedition in 1923 to search and extract dinosaur fossils in the grounds of Mongolia.
George Olsen, the junior paleontologist, excavated and discovered the AMNH 6554 holotype, which is an almost complete right hind limb, on the 25th of April. With this hind limb, there were also few fragments from two manual unguals and left pes.
This group was previously called a long-armed theropod. However, Bradley and Mader in 1989 and Perle in 1977 identified that AMNH 6368's forelimbs did not share traits with Tyrannosauroidea.
The length of these dinosaurs was 16 ft (5 m). Charles Gilmore described both the species and genus in 1933.
If you liked reading these fun Alectrosaurus facts, then you need to check out these cool facts about Sauropelta and Chungkingosaurus.
Alectrosaurus Interesting Facts
How do you pronounce 'Alectrosaurus'?
The pronunciation of Alectrosaurus is 'Ahlec-tro-sore-us.'
What type of dinosaur was an Alectrosaurus?
Alectrosaurus, meaning 'unmarried lizard' or 'alone lizard', is a theropod dinosaur of the phylum Chordata. The discovery of partial Alectrosaurus olseni (Charles Gilmore) specimen material, AMNH 6368 (complete right hind limb), and AMNH 6554, were made in the Iren Dabasu Formation, current-day Inner Mongolia.
This carnivore species is a close relative of the Tyrannosaurus rex. There have been more discoveries made of the fossil material of this specimen in the same Iren Dabasu Formation.
However, the inclination of the AMNH 6556 specimen belonging to this carnivore group is not clear as this holotype lacks a hind limb material. AMNH 6556 was found in another region but in the same year.
In which geological period did the Alectrosaurus roam the earth?
The material Alectrosaurus olseni (Charles Gilmore) dates back to the Late Cretaceous period around 83-74 million years ago.
When did the Alectrosaurus become extinct?
Alectrosaurus olseni (Charles Gilmore) of the Late Cretaceous period became extinct in the mass extinction event of the Cretaceous-Paleogene period around 66 million years ago.
Where did an Alectrosaurus live?
Alectrosaurus, of the Late Cretaceous, probably lived across present-day Asia. The fossils were found in the Gobi Desert (Mongolia), Navoiy region (Uzbekistan ), Iren Dabasu Formation (Inner Mongolia). The fossil material has been discovered in both Bayan Shireh and Iren Dabasu Formation.
What was an Alectrosaurus' habitat?
This carnivore, Alectrosaurus, occurred mostly in terrestrial habitats.
Who did an Alectrosaurus live with?
It is not known if the Alectrosaurus (GIlmore, 1933) species were social or not. However, this theropod dinosaur might have lived in a group like other dinosaurs.
How long did an Alectrosaurus live?
The average or maximum life expectancy of this specimen is not known.
How did they reproduce?
The reproduction of Alectrosaurus (Dinosauria: Saurischia) was oviparous. However, the breeding process, incubation, and parental care of this specimen are not known.
Alectrosaurus Fun Facts
What did an Alectrosaurus look like?

These tyrannosaurid species were bipedal and medium-sized dinosaurs. The collected material of Alectrosaurus (Dinosauria: Saurischia) has an almost complete hind limb but lacks distal tarsal and other fragmentary elements.
When compared to other tyrannosaurids, the hind limbs of these specimens were gracile. The Alectrosaurus' skull was large and had similar features to the Tyrannosaurus rex, but smaller than the T-rex in size.
The Alectrosaurus' teeth were extremely notched. The femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone) are of the same length, which is a distinction of other tyrannosaurids with the tibia being larger than the femur.
How many bones did an Alectrosaurus have?
The total number of bones in the Alectrosaurus skeleton is not known. The partial remains that were found are a fragmentary skull, caudal vertebrae, right hind limb, partial maxilla, the right foot's metatarsal, lower jaws, and more elements.
How did they communicate?
The mode of communication of this dinosaur is unknown. However, the Alectrosaurus species might have communicated through body language, calls, and gestures.
How big was an Alectrosaurus?
The Alectrosaurus was 16-20 ft (5-6 m) in length and their height was 8 ft (2.5 m). The length of the tibia was 28.7 in (73 cm) and the femur measured up to 28.6 in (72.7 cm). Their relative, Tyrannosaurus rex, is almost twice as long and measured around 40 ft (12.3 m)!
How fast could an Alectrosaurus move?
The exact running speed of this tyrannosaurid is unknown. So, it is possible that this species was quiet and fast-moving like other bipedal dinosaurs.
How much did an Alectrosaurus weigh?
The Alectrosaurus weight range is around 1,000-2,000 lb (454-907 kg).
What were the male and female names of the species?
There is no particular name given to either the male or the female Alectrosaurus olseni yet.
What would you call a baby Alectrosaurus?
There is no specific name given to baby Alectrosaurus olseni dinosaurs yet.
What did they eat?
The diet of the Alectrosaurus olseni was carnivorous. This species might have fed in smaller dinosaurs.
How aggressive were they?
It is unknown how aggressive these tyrannosaurid specimens were.
Did you know...
Alectrosaurus vs gigantoraptor: Gigantoraptor means 'giant seizer' and Alectrosaurus means 'unmarried lizard' or 'alone lizard.' The name is a derivation of Latin terms 'gigantis' or 'gigas' means 'giant' and raptor means 'seizer.'
Gigantoraptor is over the size of Alectrosaurus dinosaur but way smaller than Tyrannosaurus measuring around 26-29 ft (8-8.9 m). Wang Jianmin, Tan Lin, Tan Qingwei, Xu, and Zhao Xijin described and named the type species Gigantoraptor erlianensis.
Some genera groups within the Tyrannosauroidea superfamily are Dilong, Moros, Timimus, and Timurlengia. Henry Fairfield Osborn came up with the name Tyrannosaurus and the family name in 1905.
This name is a combination of Greek terms, tyrannos meaning 'tyrant' and saurus and 'lizard.'
Also, the 'oidea' suffix is a Greek term derivation meaning 'form' and is commonly used Alick Walker, a British paleontologist first publish this superfamily name in the paper in 1964. This superfamily belongs to the Middle Jurassic to Late Cretaceous time period around 166-66 million years ago.
The complete name, Tyrannosaurus rex translates to 'King Tyrant Lizard' or 'tyrant lizard the king.' This name was given due to the size of these species and the recognized dominance of other species of dinosaurs.
The new species within this genus called Tyrannosaurus bataar was named by Evgeny Maleev, a Soviet paleontologist in 1955. Some subjects of debate of T. rex are potential speed, physiology, and feeding habits. T. rex was a carnivore and bipedal and had a huge skull balanced on a heavy long tail.
Where was Alectrosaurus found?
Walter W. Granger, the chief paleontologist of the American Museum of Natural History, led an Asiatic expedition in 1923 to search for fossilized dinosaur materials in regions of Mongolia. George Olsen, the junior paleontologist, discovered AMNH 6554 material, which is an almost complete right hind limb, on the 25th of April and the specific scientific name honors George Olsen.
How did Alectrosaurus get their name?
The Greek term Alectrosaurus means 'unmarried lizard' or 'alone lizard.' Charles Gilmore described and named these species combining the Greek terms for 'alone' and 'lizard' (saurus).
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly dinosaur facts for everyone to discover! For more relatable content, check out these Puertasaurus facts and Yinlong facts for kids.
You can even occupy yourself at home by coloring in one of our free printable Alectrosaurus coloring pages.